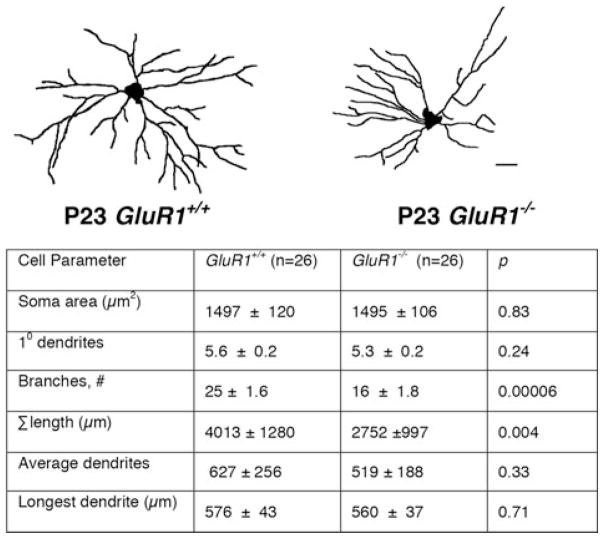
Figure 1.
Deletion of GluA1 from mice results in motor neurons with a smaller and simplified dendritic arbor (from Ref. 20). Spinal motor neurons of GluA1−/− mice compared to WT mice at P23. Mice at P23 have motor neurons with significantly fewer branches (the average WT dendritic tree has 25 ± 1.6 branches, compared to that of GluA1−/−, which has only 16 ± 1.8 branches (P < 0.0001)) and a smaller total tree size (the average dendritic tree of WT has a total length of 4013 ± 1280 μM, compared to 2750 ± 997 μM in the GluA1−/− mice (P < 0.05)). This effect is unique to the dendritic arbor, in that motor neuron soma size remains unchanged.