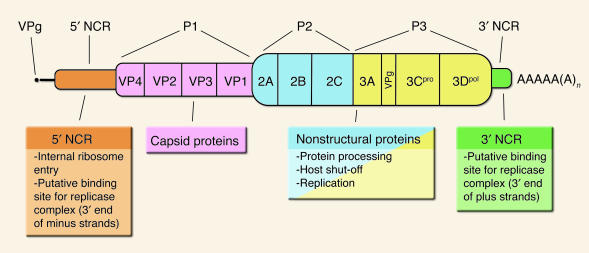
Figure 1.
Functional map of the poliovirus genome. Genomic RNA is linked to a virus-encoded peptide (VPg) at the 5′ end and a genetically coded poly(A) tract at the 3′ end. Viral RNA is depicted with a description of the functions of the various regions of the genome. The coding region of the virus is conventionally divided into three sections, referred to as P1, P2, and P3. The P1 region encodes the structural (capsid) proteins. The P2 region encodes proteins required for RNA replication and one of the viral proteinases responsible for host cell shut-off of cap-dependent translation. The P3 region encodes the major viral proteinase (3Cpro), the viral RNA_dependent RNA polymerase (3Dpol), and other proteins required for RNA replication. The coding region is preceded by an unusually long 5′ NCR, which directs translation initiation by internal ribosome entry in the absence of cap-dependent functions. The viral genome also contains a short 3′ NCR, which presumably contains cis-acting sequences involved in template recognition by the viral-replication initiation complex.