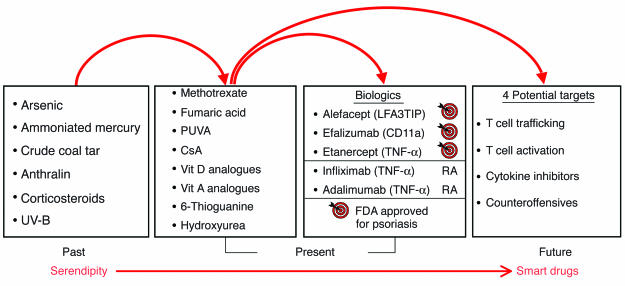
Figure 2.
Translational arcs of discovery in psoriasis. In the past, therapeutic agents used by dermatologists were generally discovered serendipitously. Current therapeutic agents are characterized by more specific targeting of defined molecules in the pathological pathways, including, most recently, the use of biologics, which target T cells (alefacept, efalizumab, and etanercept; approved by the US Food and Drug Administration [FDA] for the treatment of psoriasis), and TNF inhibitors (etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab; approved by the FDA for the treatment of RA). Several agents listed (Past column), including corticosteroids and UV-B light, are still currently used by some dermatologists to treat psoriasis patients. Future drug development should provide additional smart drugs that target specific molecular mediators implicated in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Note: Biologics are defined as therapeutic agents produced by organisms through the use of recombinant biotechnology. CsA, cyclosporin A; PUVA, psoralen and UV-A light therapy; Vit, vitamin.