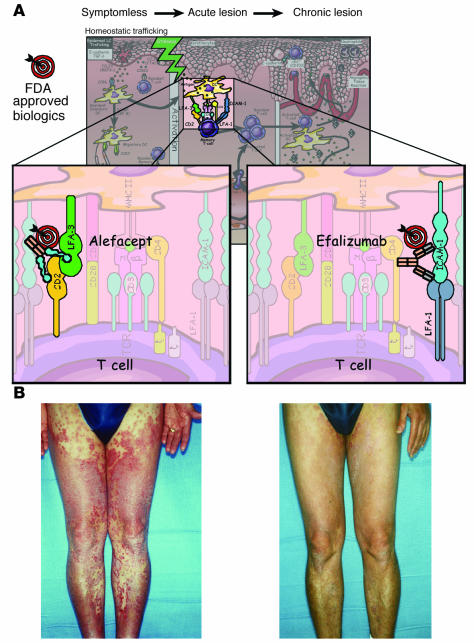
Figure 5.
(A) T cell_targeted therapies in psoriasis. Two FDA-approved biologics (alefacept and efalizumab) are portrayed; the molecular target is identified on the T cell surface (upper panels). Note that the site of action of these agents is depicted in the skin, but the therapeutic efficacy may include other anatomical sites such as lymph nodes or other secondary lymphoid tissues. Alefacept targets the CD2:LFA-3 ligand/receptor interactions, whereas efalizumab targets the LFA-1:ICAM-1 ligand/receptor pair of surface molecules expressed by T cells and APCs, respectively. (B) The clinical response of a patient with severe psoriasis (left) to efalizumab administered for 2 months. Note the almost complete clearing of lesions on the lower extremities and hand (right).