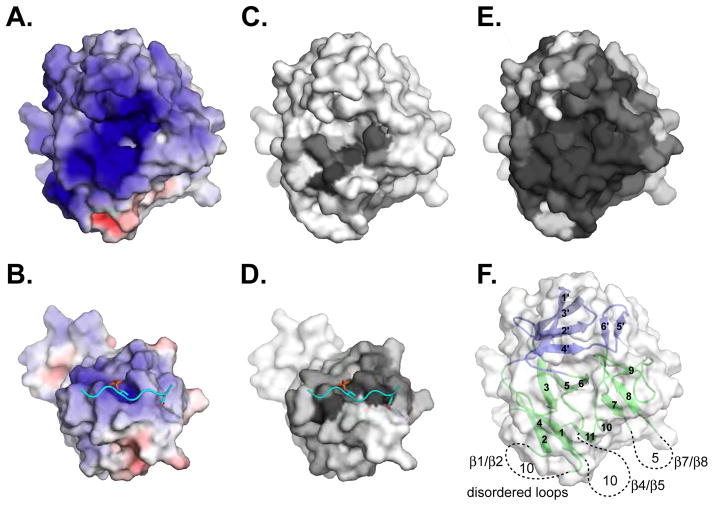
Figure 7. Features of the Pellino2 substrate-binding surface.
Surface representations are shown of the Pellino2 FHA-like domain and of the Rad53 FHA1/Rad9 complex in the same orientation as Fig. 6.
(A) The substrate-binding pocket on Pellino2 is highly electropositive, substantially more than the equivalent region of the Rad53 FHA-1 domain (B). The electrostatic potential at the solvent accessible surface, calculated using APBS (Baker et al., 2001), is projected onto a molecular surface, and colored in a gradient (red-white-blue) from −6kT to +6kT.
(C–E) Amino acid conservation is projected onto the same molecular surfaces using the program CONSURF (Landau et al., 2005). A gradient from grey to white represents most conserved to most divergent positions. Conservation taken from: (C) a structure based alignment of Pellino2 to all FHA domains of known structure, (D, E) pfam alignments of (D) all FHA domains or (E) all Pellino proteins.
(F) In view of the Pellino2 FHA domain the location and length of the disordered loops are represented with dashed lines.