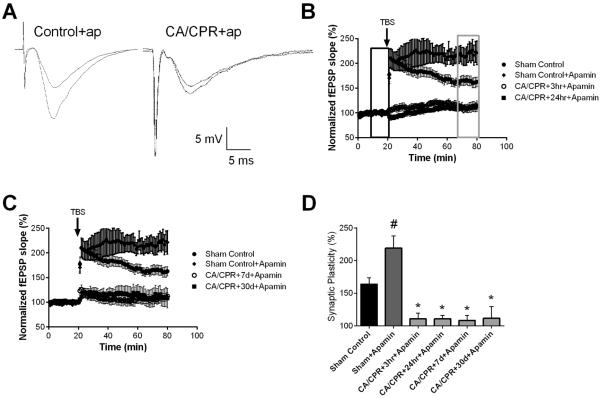
Figure 5.
Ischemia impairs SK2 channel dependent plasticity. A) Example fEPSPs from sham operated control and 30 days after CA/CPR mice in the presence of apamin before (black) and after (grey) TBS. B) Time course of fEPSP slope (mean ± SEM) from sham mice under control conditions (solid circles) and in the presence of 100 nM apamin (diamonds). Time course of fEPSP slope recorded in the presence of 100 nM apamin from mice 3 hrs (open squares) or 24 hrs (solid squares) after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR). Arrow indicates timing of theta burst stimulus (TBS; 40 pulses). C) Time course of fEPSP slope (mean ± SEM) from sham (solid circles) and in the presence of apamin in sham (diamond), mice 7 days (open squares) or 30 days (solid squares) after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CA/CPR). Arrow indicates timing of theta burst stimulus (TBS; 40 pulses) CD) Quantification of change in fEPSP slope following TBS. Average fEPSP slope (mean ± SEM) 60 minutes after TBS (in grey box in B normalized to baseline (black box in B). * P < 0.05 compared to sham controls.