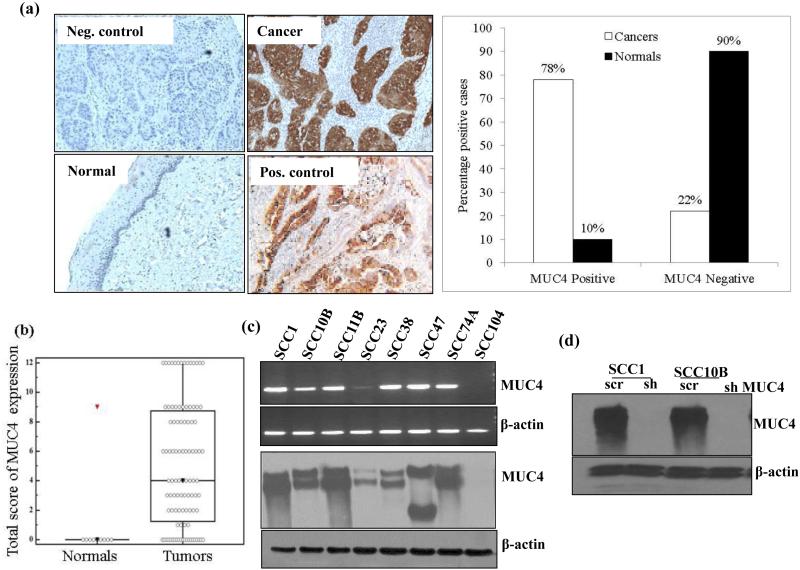
Figure 1.
Over expression of MUC4 in HNSCC tissues and HNSCC cell lines. (a) Immunohistochemical analysis of MUC4 paraffin embedded sections of normal tissues (n = 10) and HNSCC tissue (n = 87) using anti-MUC4 Mab 8G7. Anti-KLH Mab K2G6 was used as negative control. Pancreatic cancer tissue sample was used as positive control for MUC4 expression. Magnification × 100. (b) Box plots showing distribution of composite scores based on IHC of MUC4 protein. Increased expression of MUC4 was observed in HNSCC with a median score of 4 (range 0–12), as compared to the histologically normal oral tissues with a median score of 0. (c) MUC4 expression in a panel of HNSCC cell lines was determined at protein level by immunoblotting while mRNA was analyzed by RT-PCR. β-actin was used as loading control for both western blot and RT-PCR analysis. (d) Silencing of MUC4 expression in SCC1 and SCC10B cells. Cells were infected with lentiviruses carrying shRNA against MUC4 in pLKO.1 hairpin vector or with scrambled sequence containing vector and used as control. Transfected cells were selected using Puromycin and positive clones were checked for MUC4 expression using 2% agarose SDS gel. β- actin was used as a loading control.