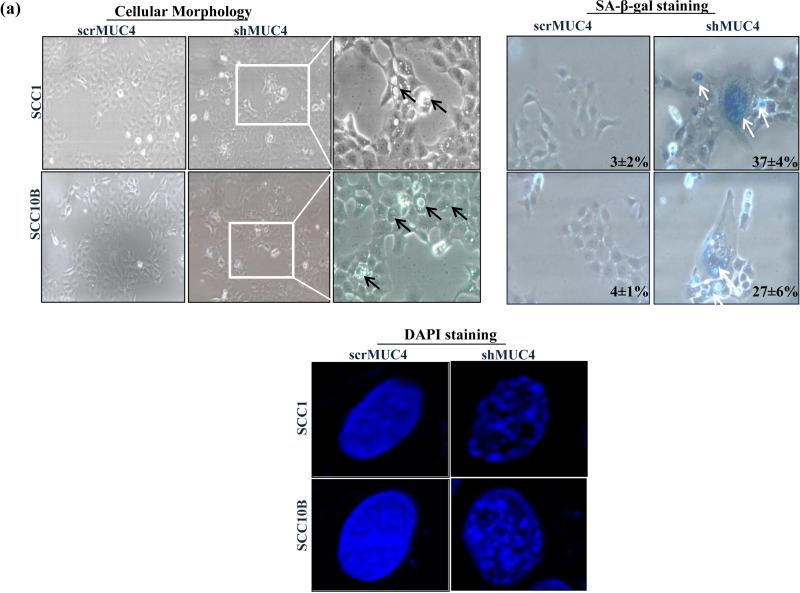
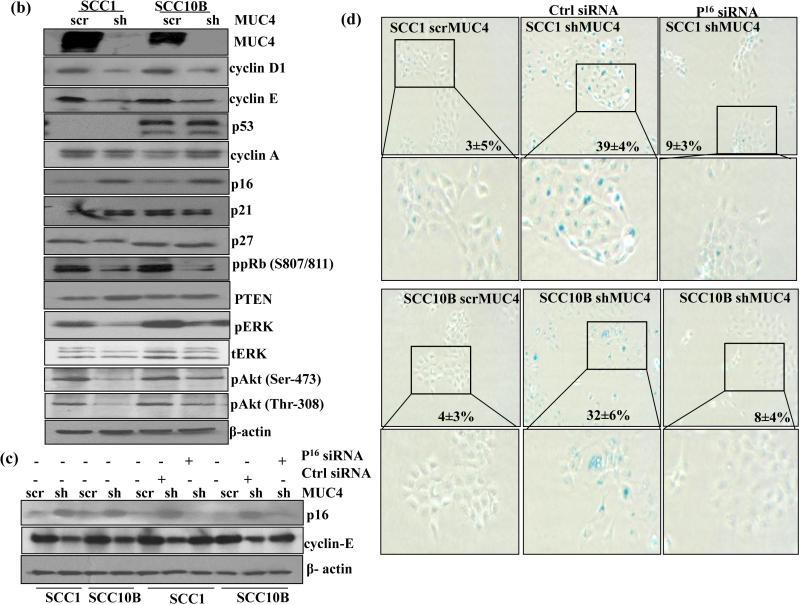
Figure 3.
MUC4 knockdown induces cell senescence by modulating cell cycle regulators proteins in HNSCC cells. (a) HNSCC cells were subjected to cellular morphological observation, SA-β-gal and DAPI staining and observed under microscopy. MUC4 KD caused SCC1 and SCC10B cells are large, flattened and vacuolated, characteristics of senescent cell. SA-β-gal positive cells for senescence and DAPI for SAHF formation cells were observed under microscope and quantified. (b) Protein lysates from control and MUC4 KD HNSCC cells were analyzed for p16, p21, p27, p53, cyclin D1, cyclin E, cyclin A PTEN, phosphorylated and total Akt, ERK1/2 proteins. Western blot analysis showed upregulation of p16 and downregulation of cyclin D1, cyclin E, pAkt and pERK1/2 with no change in expression of total Akt and ERK1/2. β-actin was used as a loading control. (c-d) p16 depletion partially rescues senescent phenotype and induces cyclin E expression. MUC4 KD SCC1 and SCC10B cells were transfected with p16 siRNA or with control siRNA. After 72 hrs, proteins lysates were analyzed for p16, cyclin E expression and stained for SA-β-gal positive cells. β-actin was used as a loading control for western blot analysis.