Fig. 2. ILK is Required for Granule Polarization Toward S2–ICAM-1 Cells.
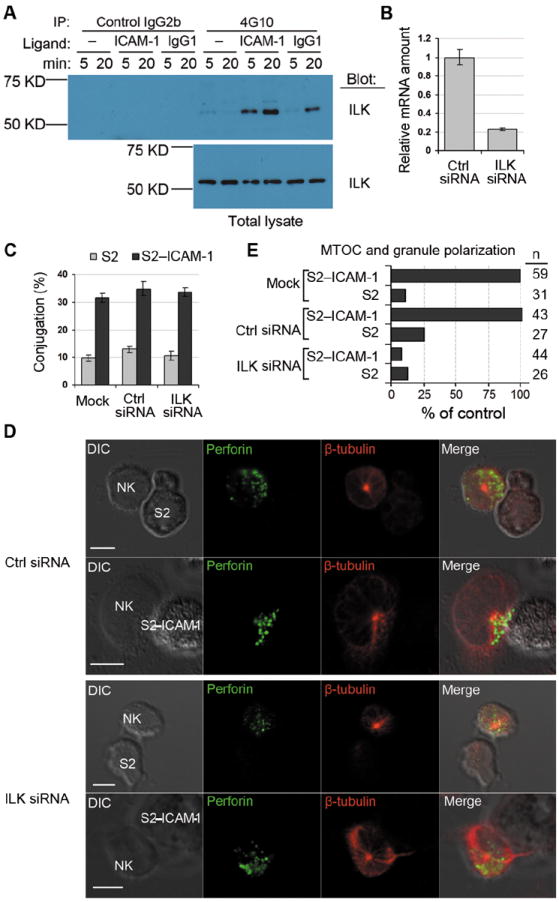
(A) Primary NK cells were stimulated with BSA only (–), ICAM-1, or human IgG1 for 5 and 20 min, as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with isotype control IgG2b agarose or with 4G10-agarose. Samples eluted with sodium phenyl phosphate (Top panel) and total cell lysates (Bottom panel) were immunoblotted with anti-ILK mAb. (B) ILK mRNA abundance 48 hours after silencing with siRNA, relative to ILK mRNA in cells treated with control (Ctrl) siRNA. Data shows 3 experiments with mean ± SD. (C) Conjugateformation of NK cells with S2 and S2–ICAM-1 cells after ILK silencing. Cells were either mock transfected or transfected with control (Ctrl) or ILK siRNA. Data shows 3 experiments with mean ± SD. (D) Representative images of MTOC and granule polarization toward S2 or S2–ICAM-1 cells. Cells were fixed, permeabilized and stained with mAb to perforin (IgG2b) and β-tubulin (IgG1) followed byisotype-specific Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated and Alexa Fluor 647-conjugatedsecondary antibodies. Scale bar = 5 μm. (E) Quantitative analysis of MTOC and granule polarization toward S2 and S2–ICAM-1 cells in NK cells treated as in (C). n represents individual NK–S2 cell contacts.
