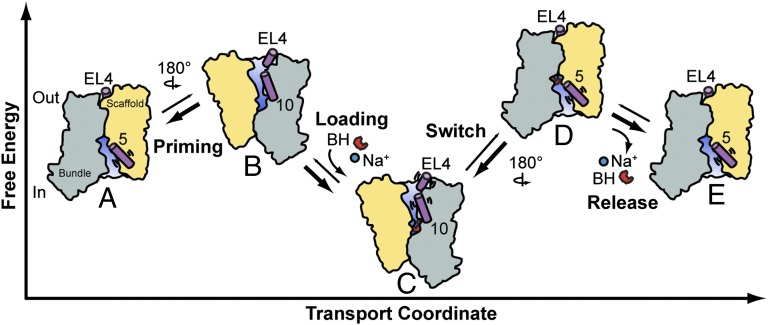
Fig. 5.
Model of Mhp1 transport. Apo-Mhp1 (A), through low probability transitions, samples outward-facing conformations (priming, B), allowing the simultaneous binding of the Na+ and substrate (loading), and resulting in a stabilization of the outward-facing conformation (C). Low-probability fluctuations allow sampling of the inward-facing conformation (switch, D) where, driven by its concentration gradient, Na+ dissociates to the intracellular solution (release). In the absence of bound Na+, BH affinity to Mhp1 is reduced, which drives dissociation of BH to the intracellular side (E). The cycle continues through the isomerization of apo Mhp1 from inward-facing (A) to outward-facing (B).