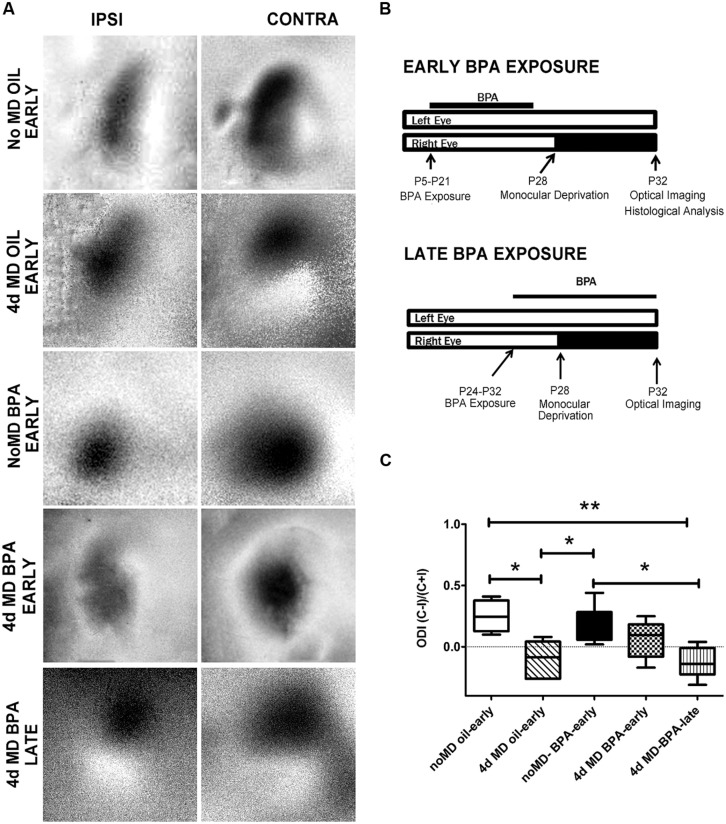
FIGURE 1.
Ocular dominance plasticity is attenuated in BPA-exposed mice. (A) Representative images of amplitude maps generated following intrinsic signal optical imaging (iOS). Non-deprived mice (No MD-early) showed an expected contralateral bias (strong contralateral amplitude when compared to ipsilateral amplitude; top panel). Following 4-days of monocular deprivation (4d MD-early), there was a shift in responsiveness toward the ipsilateral eye. NoMD BPA-early treated mice showed similar amplitude maps as NoMD Oil-early mice. Following 4d MD in early exposure BPA mice (4d MD BPA-early), maps retain a contralateral bias. A normal OD shift was observed after 4d MD in late exposure mice (4d MD BPA-late). (B) Treatment paradigms for early exposure (top schematic) and late-exposure BPA mice. (C) Ocular dominance index (ODI) results for BPA and Oil treated conditions. Values above 0 represent a contralateral ocular dominance bias (expected result in normal seeing mice). Values below 0 suggest an ipsilateral bias (expected result following monocular deprivation during the critical period). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.