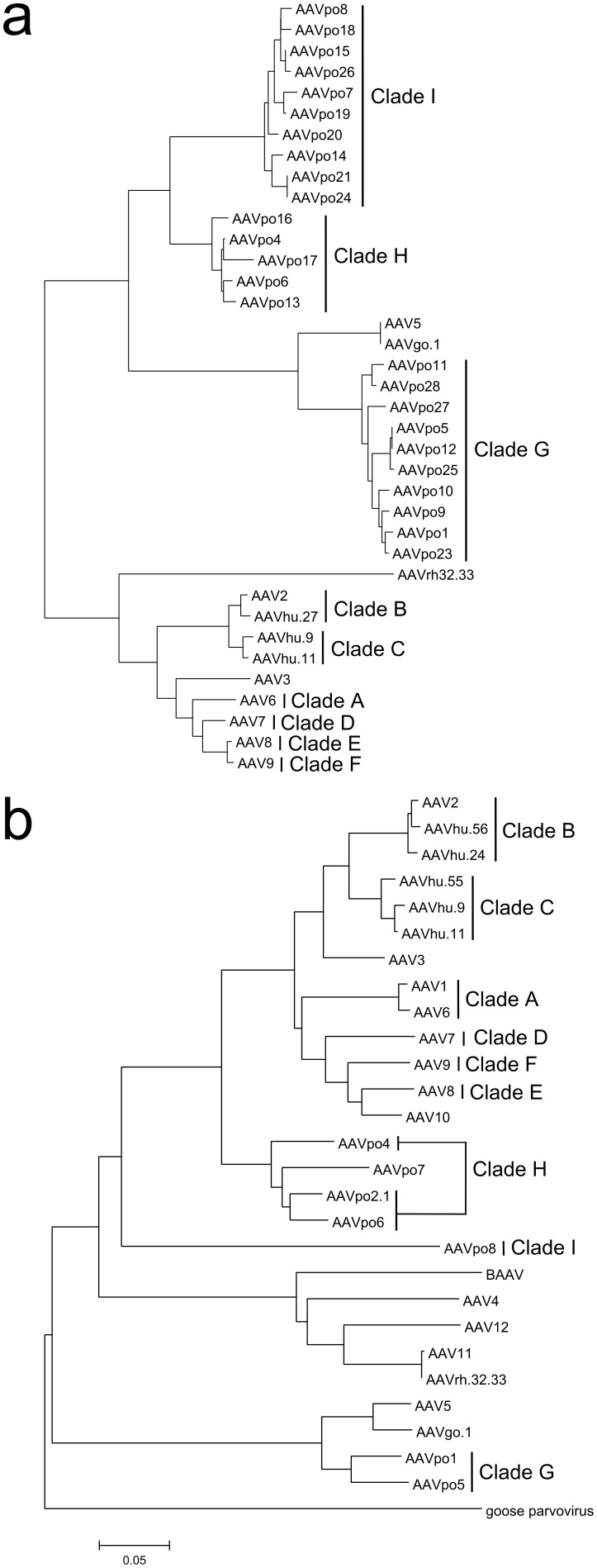
Figure 1. Porcine-derived AAVs form several new clades within the Adeno-associated virus species.
Amino acid sequence of porcine AAVs were aligned with other published AAV sequences using MUSCLE and Phylogenetic trees were inferred using the neighbor-joining method. (a) Partial sequence (~800 bp) of the beginning portion of cap was isolated from pig tissues and sequenced. The translated aa sequences were aligned with the same corresponding region of published AAV cap sequences. (b) The complete cap (~2.2 kb) of porcine-derived AAVs representing new clades were isolated by PCR and sequenced, and an alignment was performed with the published full-length cap of other AAVs. Clades are indicated by a vertical line and named in the sequential order they were identified. Figures were manipulated using Inkscape.