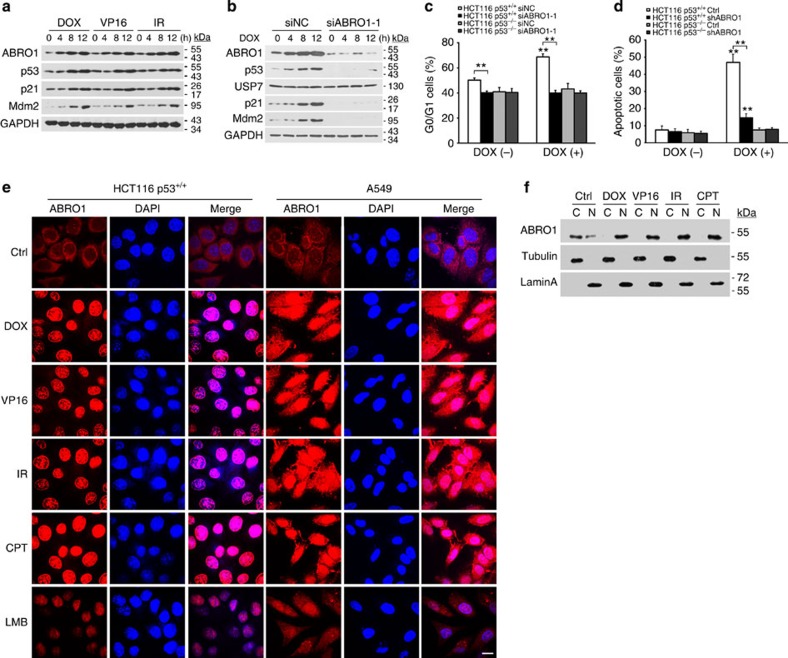
Figure 3. ABRO1 translocates to the nucleus after DNA damage and regulates the p53-dependent DNA damage response.
(a) HCT116 p53+/+ cells were treated with DOX (2 μg ml−1), VP16 (20 μM), or irradiation (10 Gy) for the indicated times. Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blotting. (b) HCT116 p53+/+ cells were transfected with siABRO1-1 or siNC. After 48 h, cells were treated with DOX (2 μg ml−1) for the indicated times. Proteins were extracted and subjected to western blotting. (c) HCT116 cells were transfected with siABRO1-1 or siNC. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were treated with DOX (2 μg ml−1) for 12 h, and cell cycle profiles were determined by FACS as described in the legend to Fig. 2. The data shown are the means±s.d. of three independent experiments and were analysed using Student’s t-test. **P<0.01. (d) HCT116 cells were infected with control lentivirus or with lentivirus encoding shRNA specific to ABRO1 and treated with DOX (2 μg ml−1) for 12 h. Cell apoptosis was examined by FACS. The values shown are the mean±s.d. of three independent experiments; data were analysed using Student’s t-test. **P<0.01. (e) HCT116 p53+/+ and A549 cells were treated with DOX (2 μg ml−1), VP16 (20 μM), IR (10 Gy) or CPT (2 μM). The subcellular localization of ABRO1 was detected by immunochemistry with ABRO1 antibody, and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used to stain the nucleus. Leptomycin B (LMB) was used as a positive control. Scale bar, 10 μm. (f) HCT116 p53+/+ cells were treated as indicated. After harvesting and fractionation of the cells, cellular fractions were blotted with the indicated antibodies. (C, cytoplasmic; N, nuclear).