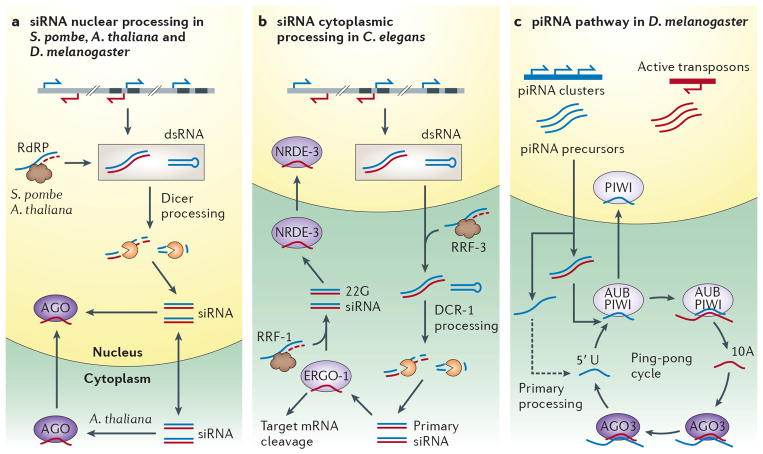
Figure 1. Generalized pathways depicting the biogenesis of nuclear small RNA.
a | siRNA processing takes place in the nucleus in S. pombe and Drosophila and the nucleoulus in Arabidopsis. dsRNA can be produced by convergent transcription, complementary transcripts, structured loci, or by RdRP activity in Arabidopsis and S. pombe. Dicer proteins generate siRNA that is loaded into an Argnoaute protein. In Arabidopsis siRNA are transported to the cytoplasm where Argonaute is loaded and then imported into the nucleus. b | In C. elegans siRNA processing occurs in the cytoplasm in a two-step fashion. Primary trigger dsRNA arises from nuclear transcription or the RdRP activity of RRF-3, which acts on transcripts in the cytoplasm. Primary processing by DCR-1 produces primary 26 nt siRNA which are loaded into ERGO-1. Loaded ERGO-1 can both facilitate PTGS in the cytoplasm and with RRF-1 generate secondary 22G siRNA siRNA. Secondary 22G siRNA is loaded into the nuclear Argonaute NRDE-3 in the cytoplasm that is then transported into the nucleus. c | piRNA biogenesis via the ping-pong cycle in the Drosophila female germline. Primary precursor piRNA antisense to active transposons (blue) is transcribed from heterochromatic piRNA clusters, and sense mRNA from active transposons (pink). In the cytoplasm primary processing generates antisense piRNA from primary precursor that is then loaded into Aub or Piwi and cleaves sense transposon mRNA to produce sense piRNA. Additional antisense piRNA is produced by Ago3 mediated cleavage of antisense primary piRNA transcripts, completing the cycle. Only loaded Piwi is imported into the nucleus.