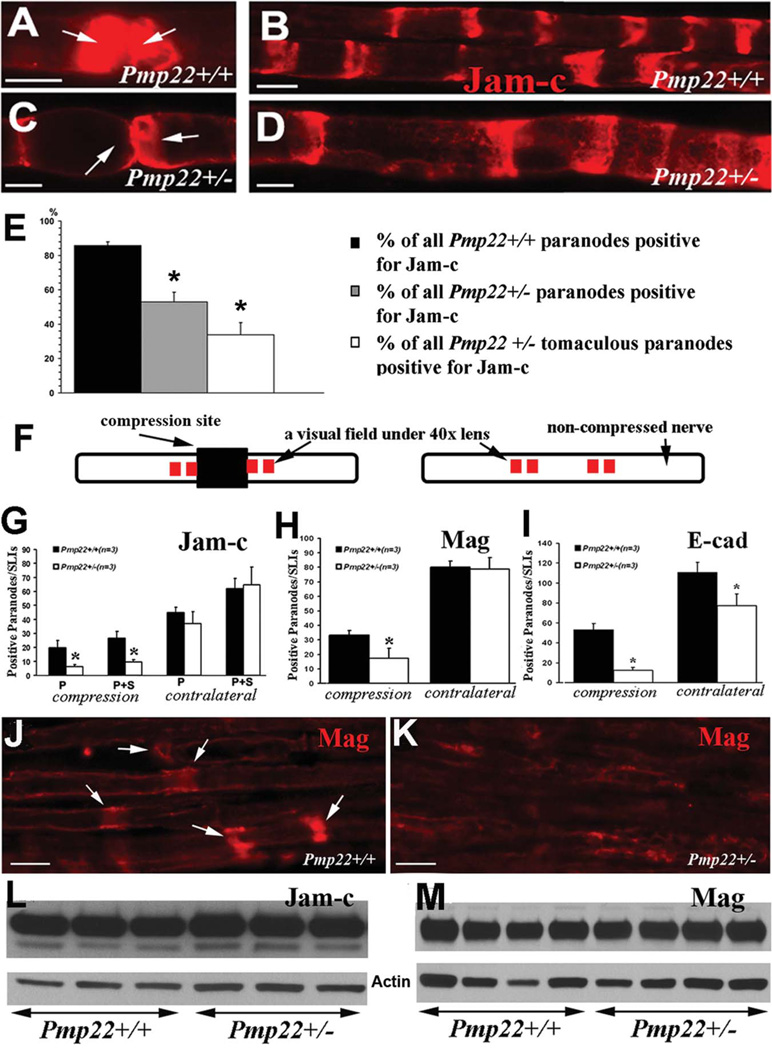
FIGURE 4.
Abnormal expression of transmembrane adhesion proteins. (A) Sciatic nerves from 5-month-old mice were teased into individual nerve fibers. A pair of Pmp22+/+ paranodes (arrows) were strongly stained by antibodies against Jam-c. (B) The Pmp22+/+ internodes contained Schmidt–Lanterman incisures (SLIs) that were stained by Jam-c. (C) Jam-c was decreased or missing in Pmp22+/− paranodes (arrows). (D) Jam-c pattern in Pmp22+/− SLIs appeared to be unchanged. (E) Percentages of paranodes positive for Jam-c were manually counted in teased nerve fibers from 3 Pmp22+/+ and 3 Pmp22+/− mice. The percentage was decreased in Pmp22+/− paranodes either with or without tomacula (*p < 0.05). (F) This diagram shows the experimental approach for data in G–K. Sciatic nerves in 3-month-old mice were compressed for 30 minutes using a vessel clamp.8 The nerves were dissected to be embedded in paraffin. The longitudinal paraffin sections were stained with antibodies against Jam-c or Mag. The compressed region is marked by a dark rectangular box. Red squares immediately adjacent to the compression site represent 4 fields imaged under a ×40 lens. All quantifications were reported in G–I. (G) Paranodes/SLIs positive for Jam-c were counted and showed no significant difference between 3-month-old Pmp22+/+ and Pmp22+/− mice (n = 3 mice for each group). However, after compression, there were fewer Jam-c–positive paranodes/SLIs in Pmp22+/− nerves than in Pmp22+/+ nerves. To avoid any false counting in paranodes/SLIs that were deformed by compression, any partially stained structures were not included in counts. P = paranodes; P1S = paranodes1SLIs (n = 3 mice for each group; analysis of variance, *p < 0.05). (H) A similar change was found for Mag (n = 3 mice for each group; t test, *p < 0.05). (I) For E-cadherin (n = 3 mice for each group; t test, *p < 0.05), the difference between Pmp22+/− and Pmp22+/+ nerves was found in either noncompressed or compressed nerves. (J) A Pmp22+/+ nerve section was stained by Mag antibodies after the nerve compression. A portion of Mag-positive SLIs were still visible. (K) In contrast, Mag-positive SLIs were hardly detectable in a Pmp22+/− nerve section after the compression. (L, M) Jam-c and Mag levels by Western blot analysis were not different between naive Pmp22+/+ and Pmp22+/− nerves (densitometry measurements: Jam-c = 0.85±0.06 in Pmp22+/+ vs 0.81±0.03 in Pmp22+/−, n = 5 mice for each group, t test, p = 0.27; Mag = 0.75±0.06 vs 0.78±0.05, n = 9 mice for each group, t test, p = 0.70). Actin bands were the loading controls. All scale bars = 10lM.