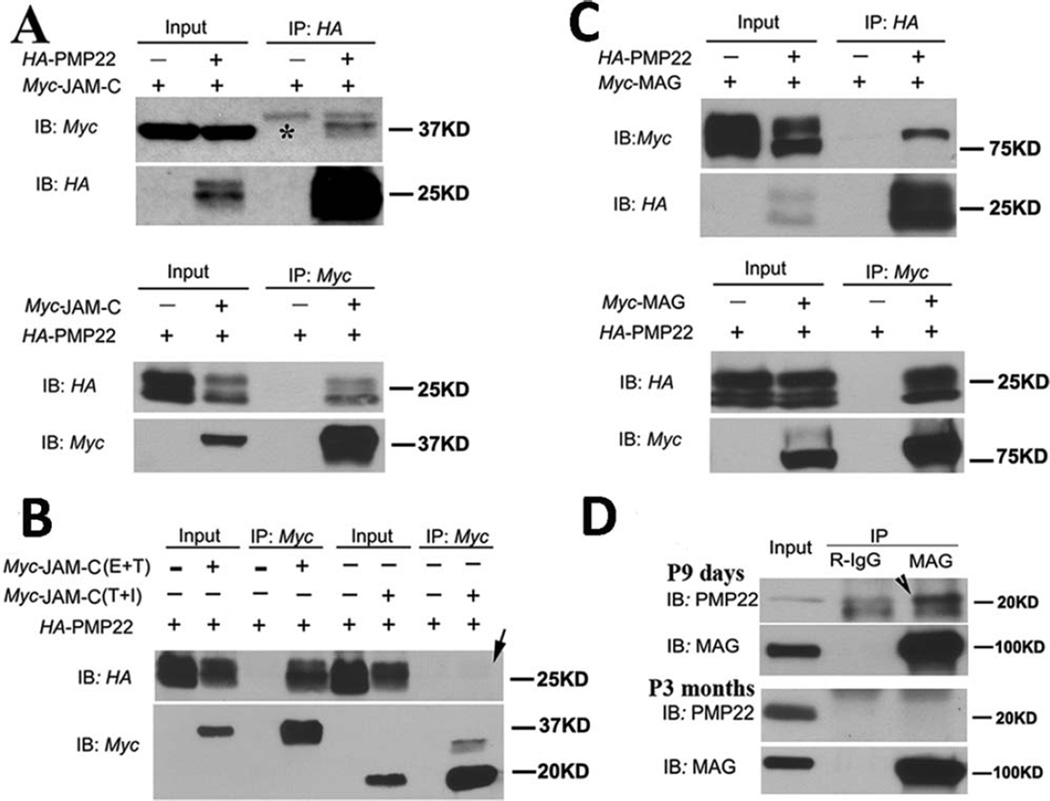
FIGURE 5.
Interactions between PMP22 and immunoglobulin (Ig) domain proteins. (A) Coexpression of human PMP22 and 1 of the Ig domain proteins (JAM-C) was done in HEK293a cells. Ten percent of cell lysates were loaded as inputs and blotted with the anti-Myc or anti-HA antibodies (Input lanes). The remaining lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with 1 of the 2 antibodies (Myc and HA). The precipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting with antibodies (IP lanes). *Heavy chain of immunoglobulin in A. IB = immunoblotting; IP = immunoprecipitation. (B) Two JAM-C mutants were respectively coexpressed with PMP22. JAM-C with an intracellular domain deletion was still able to pull down PMP22. However, JAM-C with a deletion of extracellular Ig domain failed to pull down the PMP22 (arrow in lane 8). E = extracellular domain; I = intracellular domain; T = transmembrane domain. (C) The same coimmunoprecipitation experiments were done to detect the interaction between PMP22 and MAG in HEK293a cells. (D) To examine interactions between endogenous PMP22 and MAG, lysates were extracted from mouse sciatic nerves at postnatal day 9. Mag antibodies were able to pull down endogenous Pmp22 (arrowhead), but failed to do so in 3-month-old nerves.