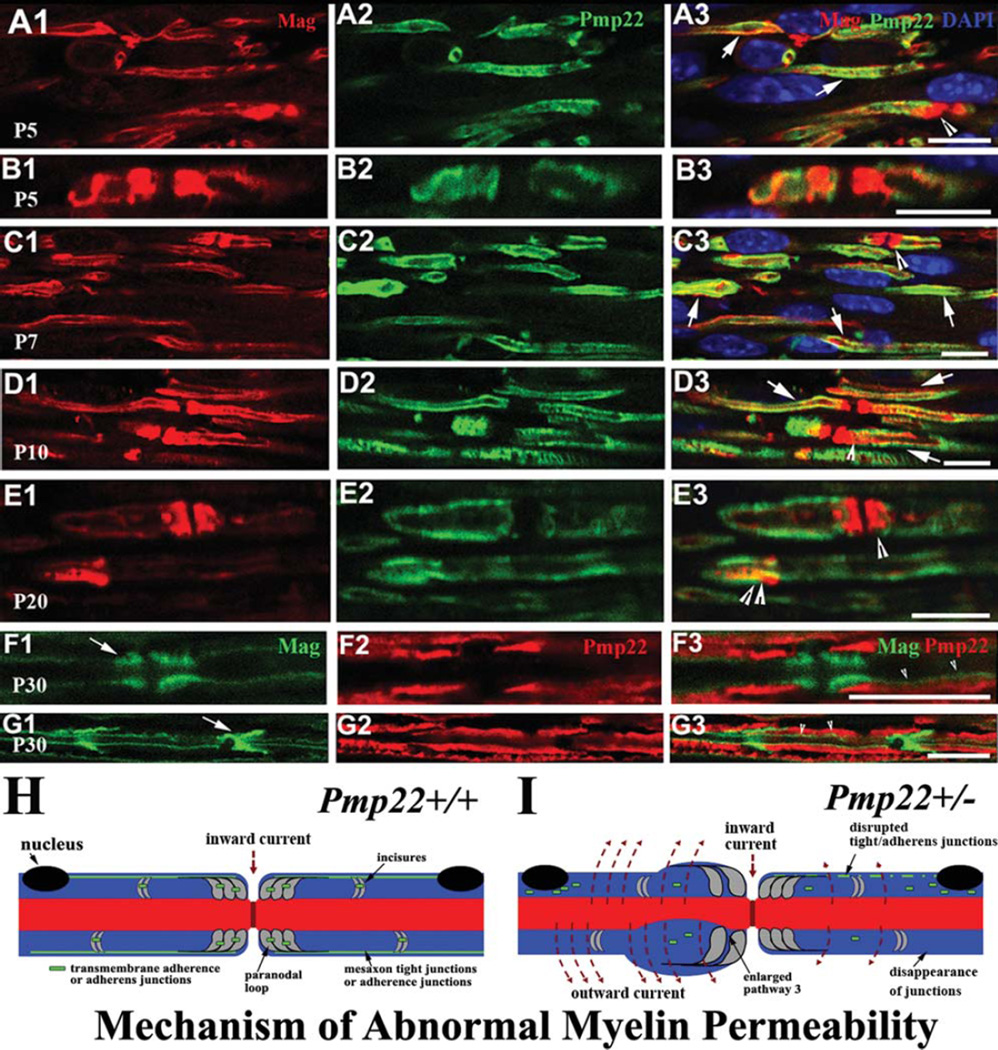
FIGURE 6.
Colocalization between Pmp22 and Mag during development. (A1–3) Wild-type sciatic nerves at postnatal day 5 (P5) were embedded in paraffin. Nerves were cut into longitudinal sections and stained with antibodies against Pmp22 and Mag. Both Pmp22 and Mag were distributed in the immature internodes and often overlapped (arrows in A3). Paranodes positive for Mag were detectable (arrowhead in A3). Pmp22 was seen in some premature paranodes and overlapped with Mag (arrowhead in A3). (B1–3) Another pair of P5 paranodes contained the colocalized Pmp22 and Mag. Notice that Pmp22 was overlapped with Mag in nearly the entire paranode on the left, but only partially occupied the paranode on the right. (C1–D3) These colocalizations were also found in P7 and P10 mouse nerves (arrows or arrowheads in C3 or D3). (E1–3) By P20, Pmp22 and Mag were better confined into internodal compact myelin and noncompact regions. However, a partial overlapping of the 2 proteins was still detectible in a paranode (single arrowhead in E3) and Schmidt–Lanterman incisure (SLI; double arrowheads in E3). (F1–G3) By P30, Pmp22 and Mag were well separated. Pmp22 was in internodal compact myelin (F2 and G2). Mag was restricted into paranodes (arrow in F1), SLIs (arrow in G1), and inner mesaxons (arrowheads in F3 and G3). (H, I) Diagrams show our proposed mechanisms. (H) Myelin junctions in Pmp22+/+ nerve are depicted in paranodes, SLIs, and mesaxons. These junctions prevent axonal current from leaking out. (I) Nerve fiber with Pmp22 deficiency develops a tomacula in the left paranode, but no demyelination. However, junction protein complexes are disrupted or disappeared in paranodes, SLIs, and/or mesaxons. These junction proteins may be found in aberrant locations, including perinuclear regions or tomaculous myelin. Abnormal assembly of these junctions in Pmp22 deficiency loosens adhesion between myelin lamellae and between other myelin junctions, thereby increasing myelin permeability without demyelination. Notice that pathway 3 is demarcated by 2 adjacent paranodal loop laminae and axolemma. Therefore, pathway 3 is subject to the regulation of transmembrane adhesion proteins, such as Jam-c.17 Pathway 3 is likely enlarged to increase myelin permeability in Pmp22+/− nerve.