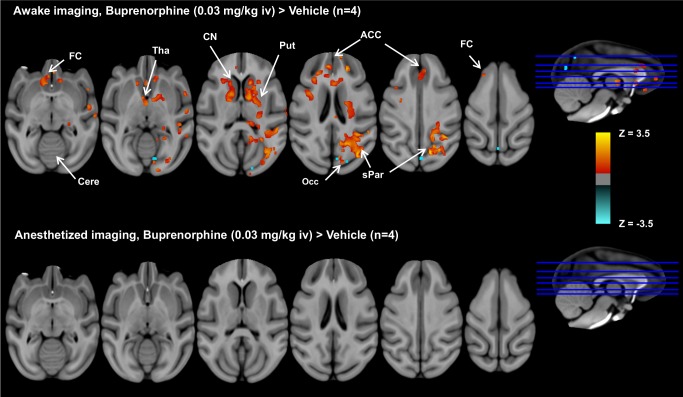
Figure 5. Group comparisons of brain activation patterns between buprenorphine and vehicle under awake and anesthetized imaging.
Group comparisons of brain activation patterns showing significant effect of buprenorphine versus vehicle (paired t-test, p<0.05, n = 4) under awake and anesthetized imaging. In the awake study, buprenorphine activates brain regions with a high density of µ-opioid receptor, including frontal cortex (FC), thalamus (Tha), anterior cingulate cortices (ACC), caudate nucleus (CN), putamen (Put), and superior parietal lobule (sPar), and limited deactivation was found in occipital cortex (Occ). In contrast, no significant difference in brain activation between buprenorphine and vehicle infusion was observed in anesthetized animals.