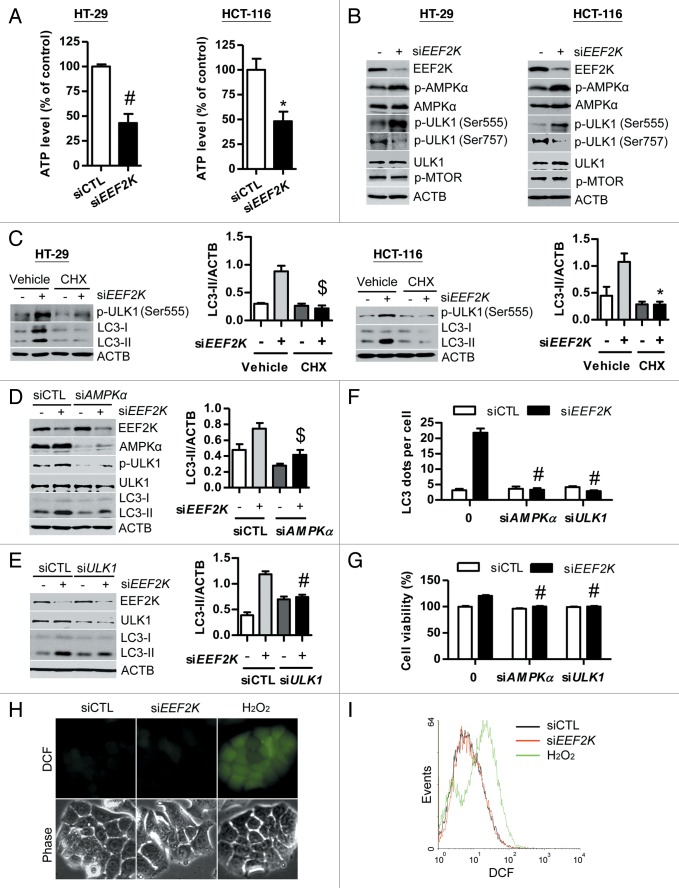
Figure 6. The AMPK-ULK1 pathway is required for autophagy induced by EEF2K silencing. (A and B) HT-29 or HCT-116 cells were transfected with nontargeting control siRNA (siCTL) or EEF2K siRNA (siEEF2K) for 48 h. (A) Silencing of EEF2K reduces ATP level. After transfection, the ATP level was analyzed using the ATPlite Luminescence Assay Kit. (B) Silencing of EEF2K activates AMPK by phosphorylation at Thr172 and activates ULK1 by phosphorylation at Ser555 and dephosphorylation at Ser757, but does not inactivate MTOR. The protein levels of EEF2K, phospho-AMPKα (Thr172; p-AMPKα), AMPKα, phospho-ULK1 (Ser555; p-ULK1 (Ser555)), phospho-ULK1 (Ser757; p-ULK1 (Ser757)), ULK1, phospho-MTOR (Ser2448; p-MTOR), and ACTB were analyzed by western blot. (C) Representative western blot and densitometric analysis normalized to ACTB demonstrating the effect of cycloheximide on EEF2K silencing-induced LC3-II accumulation. HT-29 or HCT-116 cells were transfected with nontargeting control siRNA or EEF2K siRNA. At 3 h after transfection, cells were treated with 10 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) for 45 h. (D–G) HT-29 cells were transfected with control siRNA, EEF2K siRNA, PRKAA1 and PRKAA2/AMPKα siRNA (siAMPKα), ULK1 siRNA (siULK1), siEEF2K plus siAMPKα, or siEEF2K plus siULK1 for 48 h. (D) Representative western blot demonstrating the effects of AMPKα siRNA on phospho-ULK1 (Ser555; p-ULK1) and LC3-II levels induced by EEF2K silencing. Densitometric analysis normalized to ACTB demonstrating the effect of AMPKα siRNA on LC3-II levels induced by EEF2K silencing. (E) Representative western blot and densitometric analysis normalized to ACTB demonstrating the effect of ULK1 siRNA on LC3-II levels induced by EEF2K silencing. (F) The effects of AMPKα siRNA and ULK1 siRNA on LC3 dots accumulation induced by EEF2K silencing. The average number of LC3 dots per cell was counted in more than 5 fields with at least 100 cells for each group and expressed as the means ± SEM of 3 independent experiments. #P < 0.001, vs. the EEF2K siRNA group (siEEF2K). (G) The effects of AMPKα siRNA and ULK1 siRNA on the increase of cell viability induced by EEF2K silencing. Cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay. (H and I) The effect of EEF2K silencing on ROS generation. HT-29 cells were transfected with control siRNA or EEF2K siRNA for 48 h, and treated with 20 μM DCFDA for 30 min. ROS levels were detected by fluorescence microscopy (H) or by flow cytometry (I). H2O2 (1 mM) treatment for 2 h was used as a positive control group. Scale bar: 20 μm. All quantitative data shown represent the means ± SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, $P < 0.01 and #P < 0.001, vs. the siCTL group (for A), or the EEF2K siRNA group (siEEF2K; for C, D, E, and G).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.