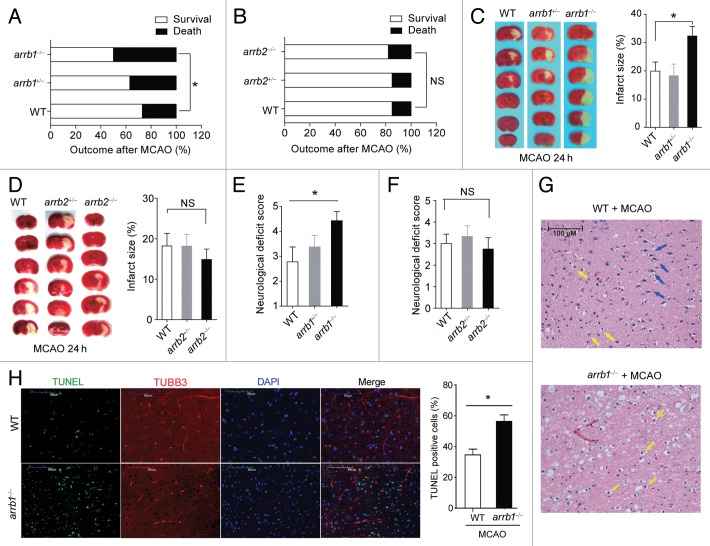
Figure 2. ARRB1, but not ARRB2, is neuroprotective in cerebral ischemia in vivo. (A and B) Mortality at 24 h after MCAO was increased in arrb1−/− mice (A), but not in arrb2−/− mice (B). *P < 0.05, determined by the Chi-Square Test. n = 15 to 32. NS, no significance. (C and D) Infarct size in arrb1−/− (C) and arrb2−/− mice (D) was measured by 2, 3, 5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining (white). *P < 0.05, determined by ANOVA. n = 6 to 9. NS, no significance. (E and F) Neurological deficit score in arrb1−/− (E) and arrb2−/− mice (F). *P < 0.05, determined by Kruskal-Wallis test. n = 6 to 9. NS, no significance. (G) Hematoxylin and eosin staining showing the morphological characteristics of WT and arrb1−/− mouse brains upon MCAO. Shrunken neurons with pyknotic nuclei are indicated with yellow arrows while intact neurons are indicated with blue arrows. (H) TUNEL analysis showing the apoptotic cells in penumbra of WT and arrb1−/− mouse brain upon MCAO. TUBB3 was stained to show axons of neurons. n = 7. *P < 0.05, determined by t test.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.