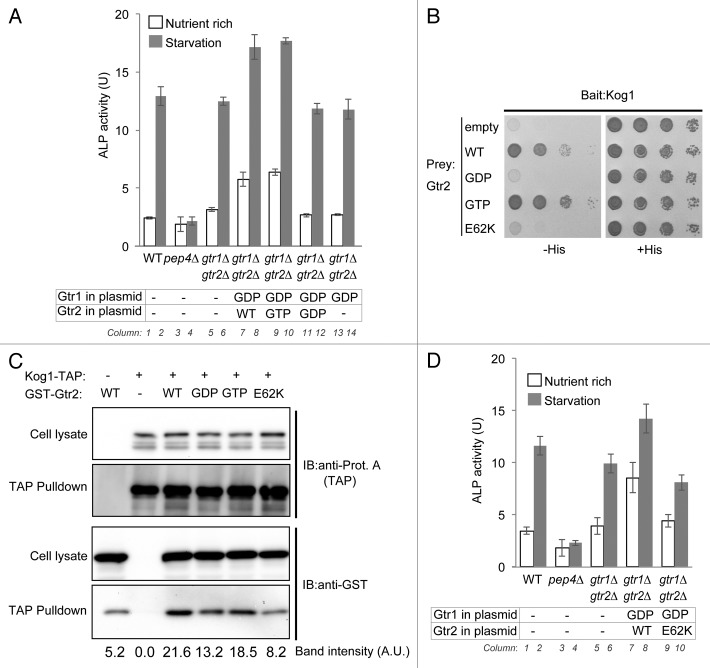
Figure 5. Gtr2 interacts with Kog1 and inactivates TORC1. (A) Wild-type (SKY084), pep4∆ (SKY100), and gtr1∆ gtr2∆ double-mutant cells harboring empty vector (-), and gtr1∆ gtr2∆ cells harboring the GDP-bound mutant Gtr1 (top row: GDP) along with wild-type, GTP-bound mutant, or GDP-bound mutant Gtr2 (bottom row: WT, GTP, and GDP, respectively), were either grown in SD medium supplemented with 0.5% casamino acids or starved of nitrogen for 3 h, and then subjected to ALP assays. Data represent means ± standard deviation from 3 independent experiments. (B) Cells of the strain for yeast 2-hybrid analysis (PJ69-4A) harboring pGBD-C1 vector encoding wild-type, GTP-bound mutant, GDP-bound mutant, or E62K mutant Gtr2 (pSK150, pSK151, pSK152, or pSK222, respectively) and pGAD-C1/Kog1 (pSK156) were serially 10-fold diluted and spotted onto SC medium plates either lacking histidine and leucine or histidine, leucine, and uracil. Results after 2 d of culture at 30 °C are shown. (C) Cells endogenously expressing TAP-tagged Kog1 and harboring multicopy vector encoding wild-type, GTP-bound mutant, GDP-bound mutant, or E62K mutant Gtr2 were subjected to TAP affinity isolation assays. The lysates and the affinity isolates were subjected to western blot analysis with anti-protein A and anti-GST antibodies. (D) Strains (wild-type, SKY084; pep4∆, SKY100; and gtr1∆ gtr2∆, SKY167) harboring empty vector (-), and gtr1∆ gtr2∆ (SKY167) harboring GDP-bound Gtr1 mutant (GDP) along wild-type (WT) or E62K mutant Gtr2E62K, were either grown in SD medium supplemented with 0.5% casamino acids or starved of nitrogen for 3 h, and then subjected to ALP assays. Data represent means ± standard deviation from 3 independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.