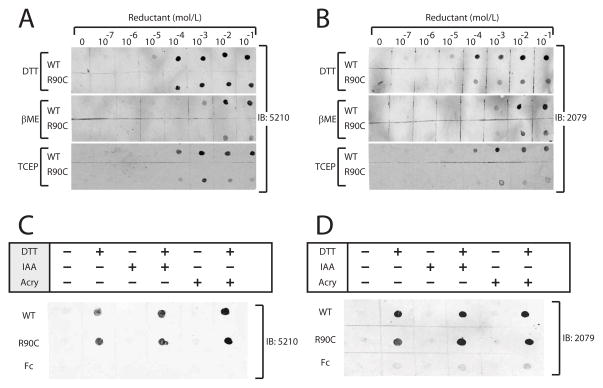
Figure 5.
Effect of reducing reagents on N-terminal epitopes in NOTCH3. As in Figure 4, purified recombinant NOTCH3 ectodomain fused to mouse Fc were treated prior to application to nitrocellulose filters. Proteins were treated with increasing concentrations of indicated reducing agents for 60 minutes at 37°C. Antibody binding to wild type NOTCH3-Fc (WT) and R90C NOTCH3-Fc (R90C) protein is shown. Similar results were obtained with the 5210 (A) and 2079 (B) antibodies. Chemical used to treat protein include thiol reductants dithiothreitol (DTT) and beta-mercaptoethanol (βME) and the phosphorus-based reductant tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP). (C–D) After reduction with 10mM DTT, NOTCH3 protein was alkylated with either iodoacetic acid (IAA; 100mM) or acrylamide (acry; 0.3%) and applied to nitrocellulose filters. Filters were then probed with 5210 (C) or 2079 (D). Alkylation had no effect on epitope recognition by either N-terminal NOTCH3 polyclonal antiserum.