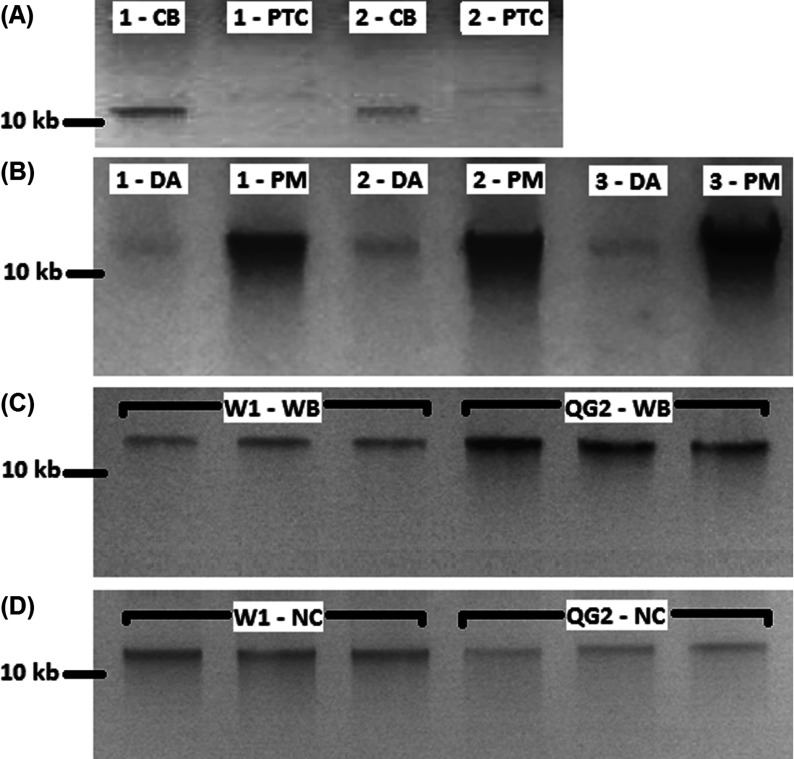
Figure 1. Gel comparison of various blood genomic DNA extraction methods.
(A) Comparison of column-based and salt-precipitation blood extraction methods. Numbers denote the volunteer for the finger-prick blood samples. CB, column-based blood extraction; PTC, salt-precipitation blood extraction protocol. (B) Comparison of premixed with W1, and direct application of cell lysate column-based blood extraction methods. Numbers denote the volunteer for the finger-prick blood samples. DA, direct application of cell lysate on column; PM, buffer W1 premixed with cell lysate prior to application on column. (C) Comparison of buffer W1 and QG2 on whole blood column-based extraction method. W1-WB, whole blood column-based extraction method premixed with buffer W1; QG2-WB, whole blood column-based extraction method premixed with buffer QG2, Extractions were carried out in triplicates. All DNA concentrations determined using IMPLEN Nanophotometer P330 were significantly different between groups in independent T test (t (16)=6.75; P=0.000), (D) Comparison of buffer W1 and QG2 on nucleated blood column-based extraction methods. W1-NC, nucleated blood column-based extraction method premixed with buffer W1, QG2-NC, nucleated blood column-based extraction method premixed with buffer QG2. Extractions were carried out in triplicates. All DNA concentrations determined using IMPLEN Nanophotometer P330 were significantly different between groups in independent T test (t (16)=6.32; P=0.000), 20 μl of DNA extracted were mixed with 6× loading dye and loaded on a 1% (w/v) TAE (Tris/acetate/EDTA) agarose gel. Samples were electrophoresed and visualized in RunVIEW by Cleaver Scientific. *Spectrophotometer readings were not shown as the majority were not detectable.