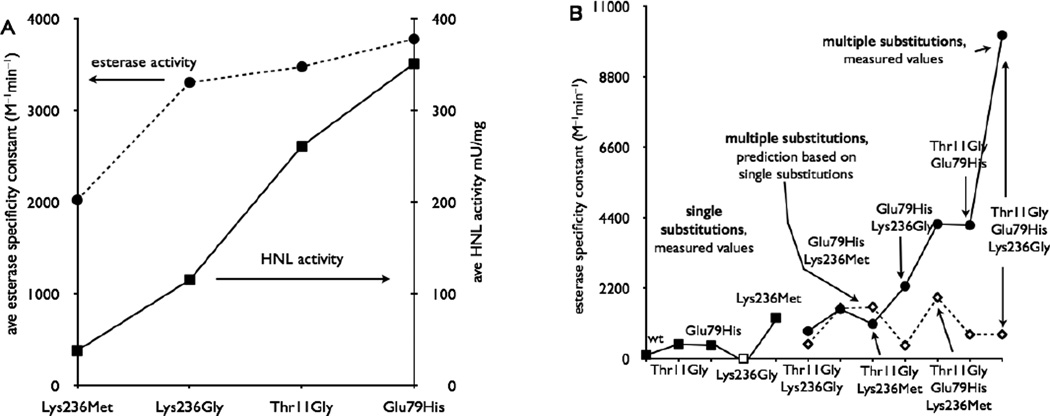
Figure 3.
Effect of substitutions in HbHNL on esterase and hydroxynitrile lyase activity. A) The average activity of variants containing the substitutions shown. The Glu79His substitution yields the largest increase in esterase activity (circles). The Lys236Met substitution caused the largest decrease in HNL activity (squares). B) Some multiple substitutions act cooperatively. The single substitutions (squares) increased esterase activity only slightly, except for Lys236Met. If these single substitutions acted additively when combined, then the esterase activity of the double and triple substitutions would be as indicated by the open diamonds. In contrast, the measured esterase activities (circles) are sometimes dramatically higher indicating positive cooperativity among the substitutions. Esterase activity refers to hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl acetate (0.3 mM, pH 7.2, 25 °C); HNL activity refers to the cleavage of mandelonitrile (5 mM, pH 5.0, 25 °C). The single substitution Lys236Gly (open square) did not yield soluble protein and was assigned a low esterase activity of < 0.5 mU/mg.