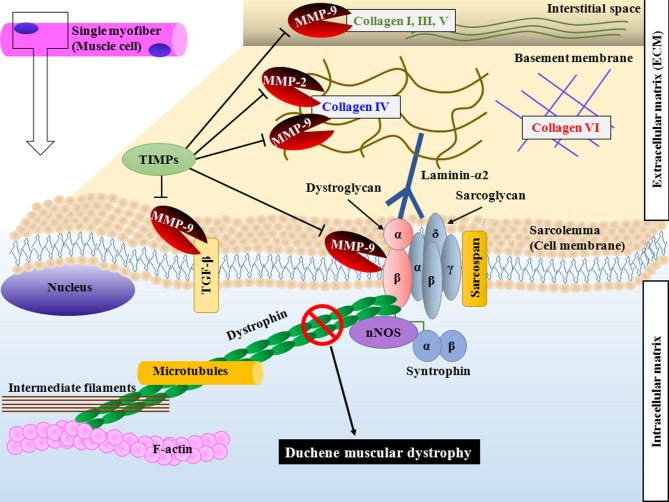
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of DGC and components of ECM targeted by MMPs in skeletal muscle. Dystrophin stabilizes muscle cells by linking F-actin, intermediate filaments and microtubules to transmembrane DGC and ECM. Loss of dystrophin causes sarcolemma instability and increases susceptibility of sarcolemma to mechanical stress. MMPs are secreted by several cell types in skeletal muscle and cause proteolysis of specific substrates. MMP-2 and MMP-9 degrade collagen type IV. MMP-9 also degrades collagen type I, III, and V in interstitial space and cleaves β-dystroglycan, an important component of DGC. MMP-9 also converts membrane-bound latent TGF-β into active form by proteolytic cleavage. Binding of TIMPs inhibits the catalytic activity of MMPs. DGC, dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex; ECM, extracellular matrix; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; TIMP, tissue inhibitor of MMPs; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.