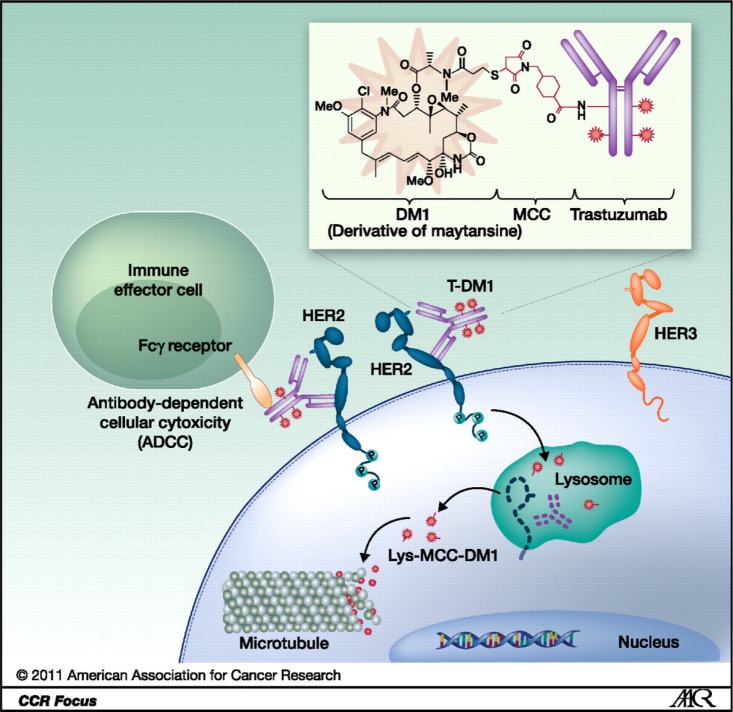
Figure 1.
Structure of trastuzumab emtansine and mechanisms of action.
Notes: On binding of trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) to human growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), T-DM1 is internalized and undergoes lysosomal degradation. This results in the release of DM1, which binds to tubulin, resulting in the suppression of microtubule dynamic instability and prevention of microtubule polymerization. T-DM1 has also been shown to retain mechanisms of action of trastuzumab, including disruption of HER2 signal transduction and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Reprinted by permission from the American Association for Cancer Research: LoRusso PM, Weiss D, Guardino E, Girish S, Sliwkowski MX. Trastuzumab emtansine: a unique antibody-drug conjugate in development for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17(20):6437–6447. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0762.41
Abbreviation: MCC, 4-[N-maleimidomethyl] cyclohexane-1-carboxylate.