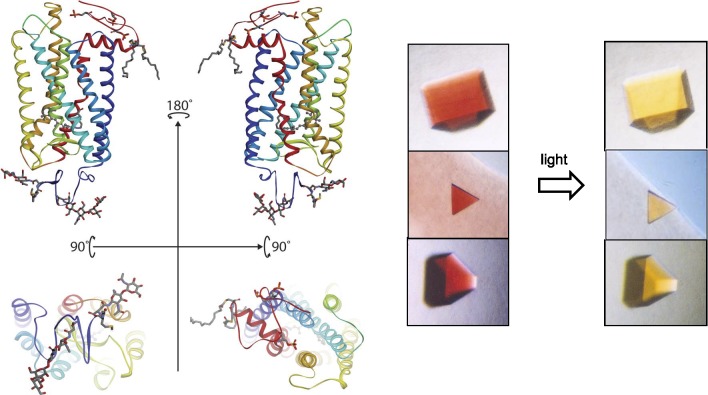
Figure 2.
Rhodopsin structure and crystals. Left top: ribbon drawings of rhodopsin (PDB accession code: 1F88)42 in the plane of a disc membrane (two views rotated by 180°). Bottom: the intradiscal side (left) and cytoplasmic side (right) of this receptor. Right: a photo-stable crystal form of the dark inactive state (left) and light-exposed activated state (right) of the receptor. Crystal pictures are reproduced from Salom D, Le Trong I, Pohl E, et al. Improvements in G protein-coupled receptor purification yield light stable rhodopsin crystals. J Struct Biol. 2006;156:497–504. Copyright © 2006 Elsevier, Inc.; Salom D, Lodowski DT, Stenkamp RE, et al. Crystal structure of a photoactivated deprotonated intermediate of rhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:16123–16128. Copyright © 2006 The National Academy of Sciences of the USA; and Salom D, Padayatti PS, Palczewski K. Crystallization of G protein–coupled receptors. Methods Cell Biol. 2013;117:451–468.299 Copyright © 2013 Elsevier, Inc., with permission from Elsevier, Inc. and the National Academy of Sciences.