Table 2.
Summaries of studies on breast density measurement with digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT)
| Author | Study method | Quality rating of study35 | Number of participants | Results/comparator | Conclusion/outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kontos et al50 | Cumulus (cohort study) | High | 52 females | Correlation between texture features on DBT vs DM, r = 0.73 Correlation of %BD vs parenchymal features 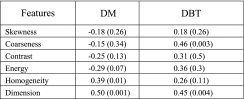
|
Cumulus is feasible for breast density measurement in DBT, and parenchymal texture features are more related to breast density on DBT than DM | |
| Kontos et al48 | Cumulus (cohort study) | High | 71 females |
Relationship %BD vs parenchymal features
|
Cumulus is reliable for breast density estimation in DBT, and parenchymal texture features are more strongly correlated with percentage mammographic density on DBT than DM | |
| Ren et al51 | Quantra (cohort study) | High | 15 projection phantom images | 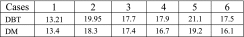 |
Quantra is a promising tool for density estimation in DBT but needs further algorithm optimization | |
| Bakic et al20 | Cumulus (cohort study) | High | 40 females | Cumulus intrauser correlation for DBT, r = 0.94 Breast density correlation for DBT vs DM, r = 0.90 |
Cumulus is very reliable for density estimation with DBT, and breast density of DM is strongly correlated with DBT | |
| Bakic et al52 | Cumulus (cohort study) | High | 35 females |
Cumulus estimated density DBT = 28 ± 19%; DM = 36 ± 20% Correlation DBT vs DM, r = 0.76 Agreement DBT vs DM, κ = 0.56 |
Cumulus is suitable for measuring breast density with DBT. Breast density is lower in DBT than in DM | |
| Bakic et al46 | Cumulus (cohort study) | High | 39 females |
Cumulus interuser correlation DBT, ρ = 0.85 DM, ρ = 0.75 Breast density with DBT vs DM ρ = 0.91; k = 0.79 |
Cumulus is suitable for density estimation on DBT, and percentage density estimated from reconstructed and projection images are similar | |
| Tagliafico et al26 |
MedDensity and BI-RADS® (cohort study) | High | 50 females |
MedDensity vs BI-RADS correlation Four-grade scale (D1–4), r = 0.54 Two-grade scale (D1–2 vs D3–4), r = 0.78 BI-RADS inter-reader agreement, k = 0.80 Breast density with DBT vs DM BI-RADS intrareader agreement, k = 0.81–0.86 BI-RADS inter-reader agreement, k = 0.91 |
Moderate breast density correlation between MedDensity and BI-RADS. Density is underestimated on DBT relative to DM | |
| Tagliafico et al47 | Cumulus and BI-RADS (cohort study) |
High | 160 females | Correlation between BI-RADS and Cumulus, r = 0.94 Cumulus density correlation between modalities MRI vs DBT, r = 0.95 DM vs DBT, r = 0.97 BI-RADS agreement for DM and DBT, k = 0.91 |
Cumulus and BI-RADS are reliable methods for estimating breast density from DBT, DM and MRI | |
| Tagliafico et al44 | MedDensity and BI-RADS (cohort study) | High | 160 females |
MedDensity vs BI-RADS correlation Four-grade scale (D1–4), r = 0.48 Two-grade scale (D1–2 vs D3–4), r = 0.76 BI-RADS inter-reader agreement, k = 0.81 Breast density with DBT vs DM BI-RADS intrareader agreement, k = 0.79–0.81 BI-RADS inter-reader agreement, k = 0.89 |
Moderate density correlation between BI-RADS and MedDensity. Breast density is lower on DBT than on DM | |
| Tromans et al53 | Volpara (cohort study) | High | 20 females | Volumetric breast density correlation for DBT vs 2D mammograms, r = 0.903 Agreement between BI-RADS and Volpara, k = 0.953 |
Volpara is robust and a promising substitute for BI-RADS | |
| Regini et al49 | BI-RADS + Quantra for DM (cohort study) | High | 200 mammograms |
Breast density with DBT vs DM BI-RADS intrareader agreement, k = 0.96 |
There is no variation in breast density assessed with DBT and DM |
BI-RADS, breast imaging reporting and data system; DM, digital mammography; k, weighted kappa agreement; κ, quadratic kappa agreement; r, correlation coefficient; ρ, Spearman's correlation.
