Abstract
We report the strategic use of cyclohexyne and the more elusive intermediate, cyclopentyne, as a tool for the synthesis of new heterocyclic compounds. Experimental and computational studies of a 3-substituted cyclohexyne are also described. The observed regioselectivities are explained by the distortion/interaction model.
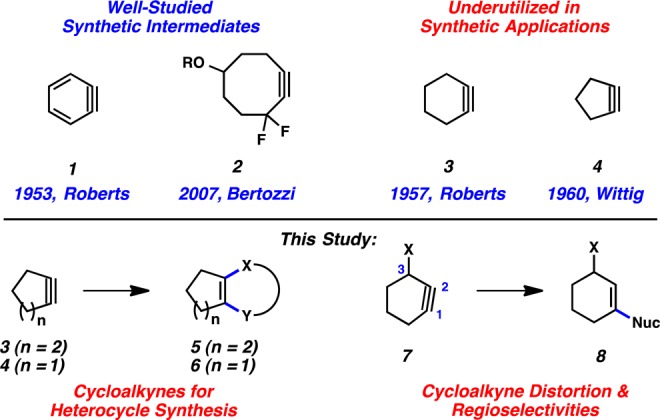
The study of small rings containing triple bonds has been a topic of vast interest for over 100 years.1 Following a provocative report in 1902 suggesting the intermediacy of an aryne,2 chemists probed the viability of benzyne (1, Figure 1) and related intermediates. Roberts, in 1953, validated the existence of benzyne (1),3 which can be used today in a host of synthetic applications.1 Perhaps the next most well-studied classes of strained alkynes are cyclooctynes (e.g., 2) and thiacycloheptynes, which have proven useful in bioorthogonal reactions by Bertozzi, Boons, and others.4 In contrast, cyclohexyne (3)5 and cyclopentyne (4)6 have seen only sparse use in synthetic applications. Breakthroughs in the manipulation of cyclohexyne include formal C–C bond insertions reported by the laboratories of Stoltz and Carreira,7,8 in addition to Diels–Alder reactions as shown by the groups of Guitián and Du Bois.9 The use of cyclopentyne has been limited to [2+2] and Diels–Alder cycloadditions.10
Figure 1.
Well-studied cyclic alkynes 1 and 2, cyclohexyne (3), and cyclopentyne (4), and objectives of the present study.
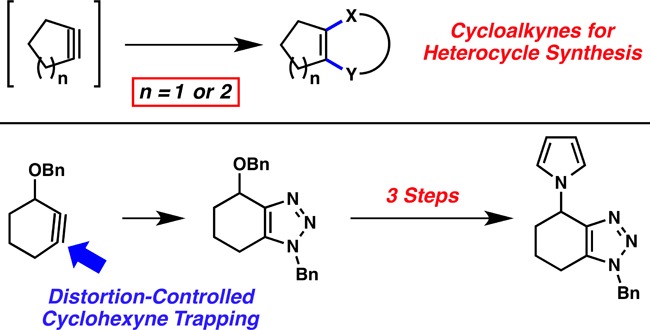
Despite the relatively limited use of 3 and 4 in synthetic applications for the construction of C–C bonds, we envisioned harnessing these strained intermediates to construct new bicyclic heterocyclic scaffolds. Heterocycles are prevalent in drugs, natural products, and other compounds of tremendous importance.11 Thus, new methods for their synthesis, especially previously inaccessible compounds, remain highly sought after. As suggested in Figure 1, cycloadditions involving 3 or 4 would provide heterocycles 5 or 6, respectively. Despite the simplicity of this approach, there are no examples of the trapping of cyclohexyne or cyclopentyne to construct heterocycles with one or more newly formed C–X bonds (where X = heteroatom). In addition, we sought to prepare a substituted cyclohexyne 7 and probe regioselectivities in both nucleophilic trapping and cycloaddition reactions. We have previously explained regioselectivities in reactions of substituted benzynes and hetarynes using the distortion/interaction model,12 but this model has not been tested on the non-aromatic cyclohexyne derivatives. Herein, we demonstrate the synthetic utility of 3 and 4 for the construction of bicyclic heterocycles, and also explain the regioselectivities seen in reactions of the first 3-substituted cyclohexyne using the distortion/interaction model.
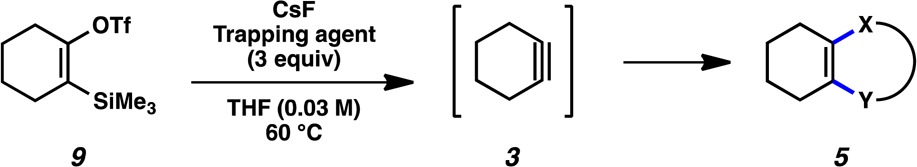
To initiate our study, we opted to generate cyclohexyne in situ from the corresponding silyl triflate, 9 (Table 1). Silyl triflate 9 was first synthesized in 1998,9a but has seen limited use, for example, in Diels–Alder reactions and formal C–C bond insertion reactions.7a,9,13,14 We were delighted to find that treatment of silyl triflate 9 with CsF in the presence of a variety of trapping agents delivered heterocyclic products in synthetically useful yields. Specifically, triazoles and pyrazoles were obtained by the trapping of azide and diazo coupling partners, respectively (entries 1–3).15 An N-Ph pyrazole was accessed using a sydnone cycloaddition (entry 4). We also explored nitrone and nitrile oxide cycloadditions, which provided isoxazoline- and isoxazole-containing products, respectively (entries 5 and 6). Moreover, additional new trapping experiments to forge 6-membered heterocycles from cyclohexyne are provided in the Supporting Information (SI). It should be emphasized that in contrast to many common methods for heterocycle synthesis, particularly benzyne trapping, the products obtained from cyclohexyne trapping possess more aliphatic character. Being able to access compounds possessing significant sp3 character is an important direction in contemporary drug discovery.16
Table 1. Cycloaddition Reactions of 3 to Construct 5-Membered Heterocycles.
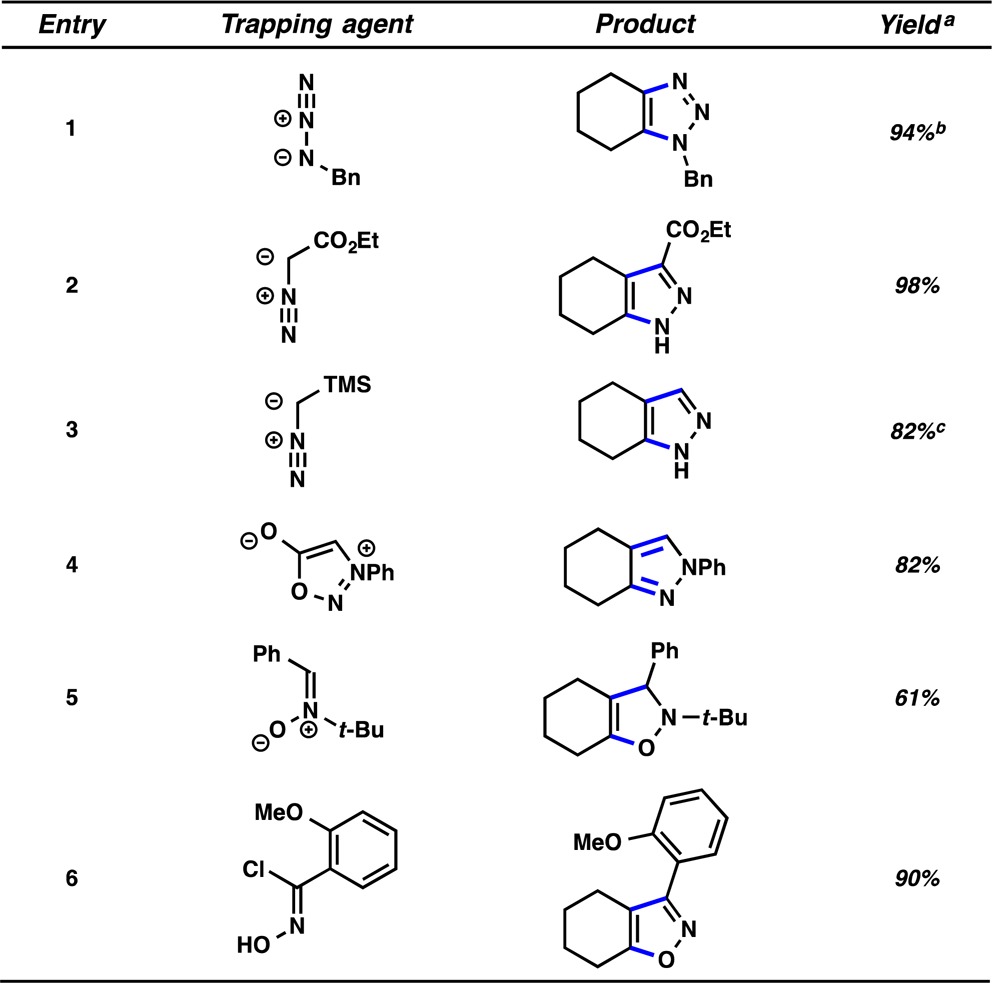
Reported yields are the average of two experiments and are based on the amounts of isolated products.
Benzene was used as a cosolvent.
Et2O was used as a cosolvent.
Encouraged by our success in building heterocycles from cyclohexyne, we performed trapping experiments of the less well-studied intermediate, cyclopentyne (4), using silyl triflate 10 (Table 2).17 Although silyl triflate 10 has been synthesized previously,18 no successful trapping experiments involving 10 have been reported. Thus, 10 was treated with CsF in acetonitrile in the presence of various trapping agents. Most trapping agents gave only low yields or none of the desired products; however, benzyl azide and sydnone partners could be employed to deliver triazole and pyrazole products, respectively (entries 1 and 2). Additionally, we found that trapping of 4 with a cyclic dimethylurea19 generated a unique product possessing a [5,7]-fused ring system (entry 3).20 Despite the limited scope of trapping agents that can be used to intercept 4, these studies validate the notion that cyclopentyne can be used in reactions beyond [2+2] and Diels–Alder cycloadditions and may react through non-radical pathways.
Table 2. Trapping Experiments of Cyclopentyne (4).
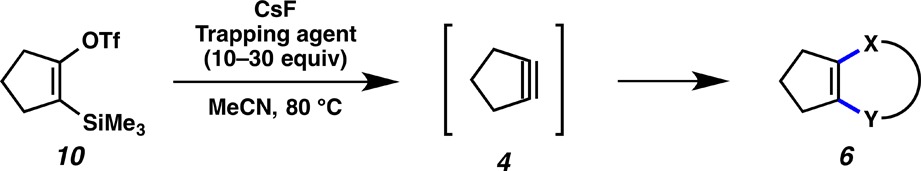
Reported yields are the average of two experiments and are based on the amounts of isolated products.
Figure 2 shows the optimized structures of cyclohexyne (3) and cyclopentyne (4) (see the SI for computational details).21 The minimum energy conformer of cyclopentyne is slightly puckered and shows Cs symmetry, in agreement with previous studies.22 The significant angle-strain of this structure is revealed by the large deviation of the internal ring angles (116°) from the ideal linear disposition of alkynes. The strain has been calculated to be ca. 74 kcal mol–1.22 Such a large strain distorts the in-plane π bond in a way that cyclopentyne has ∼10% calculated diradical character.23 The more relaxed internal angle in cyclohexyne (132°) causes a smaller, but still significant strain, estimated as ca. 44 kcal mol–1.22 Cyclohexyne (3) possesses a C2-symmetric structure that resembles the well-known half-chair structure of cyclohexene.22a,24
Figure 2.
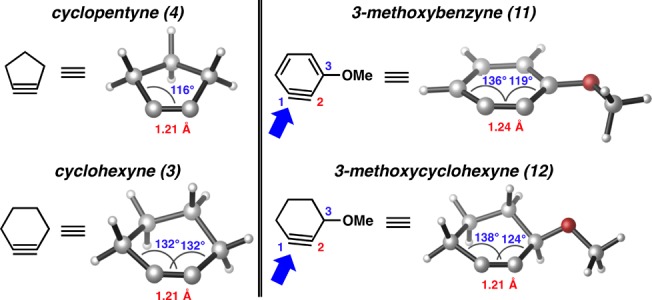
Optimized structures of 3, 4, 11, and 12 obtained using PCM(THF)/M06-2X/6-311+G(2d,p).
We also compared 3-methoxybenzyne (11) to its non-aromatic counterpart, 3-methoxycyclohexyne (12) (Figure 2). In the case of 11, as we have previously described,12a,12b the inductively withdrawing methoxy group at C3 distorts the aryne significantly. Nucleophilic trapping occurs at C1, the more linear aryne terminus whose reactive orbital possesses more p character, uniformly with high degrees of regioselectivity. Interestingly, 3-methoxycyclohexyne (12) bears similar distortion, with internal angles at C1 and C2 being calculated as 138° and 124°, respectively.25 Much like the distortion seen in 11, the distortion in 12 is attributed to the inductively withdrawing nature of the C3 methoxy group that causes rehybridization of C2 (Bent’s rule, see SI for further discussion).26 Consequently, we predict that nucleophilic addition to 3-alkoxycycloalkynes should occur with a significant preference for attack at C1, the more linear alkyne terminus.
To test our prediction, we prepared benzyloxysilyl triflate 13, the first C3-substituted cyclohexyne precursor, and performed trapping experiments (Figure 3).27 When silyl triflate 13 was treated with CsF in the presence of imidazole, adduct 15 was obtained exclusively, which arises via attack at C1 of cyclohexyne 14. Similarly, trapping with benzyl azide gave a 5.1 to 1 ratio of cycloadducts 16 and 17, which is consistent with a preference for initial bond formation occurring between the more nucleophilic terminus of the azide28 and C1 of 14.
Figure 3.
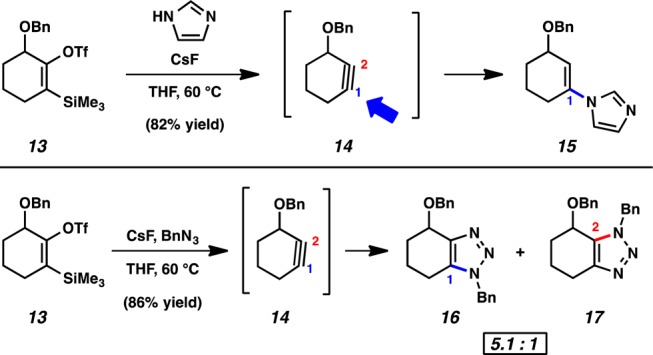
Experimental results validate regioselectivity predictions in reactions of 3-substituted cyclohexyne 14.
Figure 4 shows the calculated competing transition states, TS1–TS4, for the reactions shown in Figure 3.29 In agreement with the observed selectivity, attack by imidazole at C1 is highly preferred (by ca. 3 kcal mol–1) because 3-methoxycyclohexyne (12) is pre-distorted toward the preferred transition state, TS1. Similarly, in the azide cycloaddition, TS3 is favored over TS4, although the calculated regioselectivity is overestimated. It is important to note the systematic increase in distortion energy (ΔEdist), the cost of altering the substrate geometry toward the transition state, of the 3-methoxycyclohexyne moiety in TS2 and TS4, which accounts for most of the calculated energy differences between competing transition states. As a common feature of distortion-controlled reactions, the interaction energies (ΔEint), or in other words, the stabilization due to orbital overlap between the reacting fragments in the transition state, is nearly identical when comparing competing transition states. It is notable that this trend is observed for both the imidazole and azide trapping agents, despite their different electronic properties.
Figure 4.
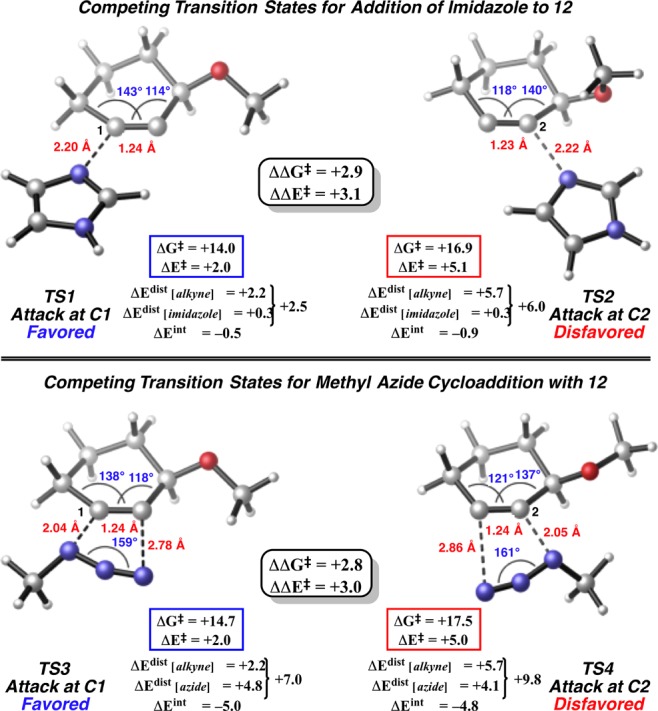
Optimized transition states for nucleophilic addition by imidazole and cycloaddition with methyl azide to 12 using PCM(THF)/M06-2X/6-311+G(2d,p). Energies are provided in kcal mol–1.
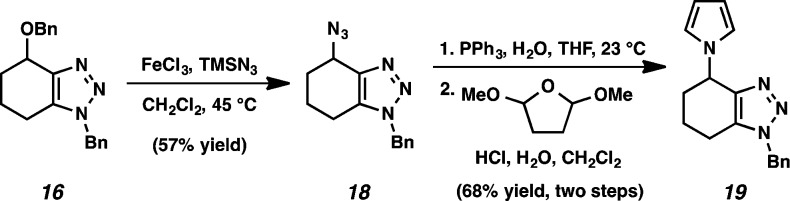
In addition to serving as a probe to assess the distortion/interaction model, benzyloxycyclohexyne 14 can also be used to access highly functionalized heterocycles. As shown in Scheme 1, triazole 16, prepared from the benzylazide cycloaddition of 14 (Figure 3), was converted to azide 18 through an uncommon functionalization of a pseudobenzylic benzyloxy group.30 Subsequent reduction and pyrrole formation provided triazolopyrrole 19.
Scheme 1. Elaboration of Benzyloxycyclohexyne 16 to Triazolopyrrole 19.
In summary, we have demonstrated that cyclohexyne and the more elusive intermediate, cyclopentyne, serve as effective tools for the synthesis of new heterocyclic compounds. We have also shown that the distortion/interaction model correctly predicts regioselectivities in reactions of the first 3-substituted cyclohexyne. This validates the distortion/interaction model as a powerful predictive tool for gauging cycloalkyne regioselectivitities, just from the reactant’s structure, while also providing the impetus for the further exploration of highly strained cycloalkynes as valuable synthetic building blocks.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the NIH-NIGMS (R01 GM090007 to N.K.G. and GM075962 to K.N.H), Bristol–Myers Squibb, the S. T. Li Foundation, the A. P. Sloan Foundation, the Dreyfus Foundation, the UC CRCC, UCLA, and the UCLA Cota Robles Fellowship Program (J.M.M.) for financial support. This work used the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE), which is supported by the National Science Foundation (OCI-1053575) along with the UCLA Institute of Digital Research and Education (IDRE). We thank Ashley Pournamdari for experimental assistance and the Garcia-Garibay laboratory (UCLA) for access to instrumentation. These studies were supported by shared instrumentation grants from the NSF (CHE-1048804) and the NIH NCRR (S10RR025631).
Supporting Information Available
Detailed experimental and computational procedures, compound characterization, Cartesian coordinates, electronic energies, entropies, enthalpies, Gibbs free energies, and lowest frequencies of the calculated structures. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Author Contributions
† J.M.M. and T.C.M. contributed equally.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Funding Statement
National Institutes of Health, United States
Supplementary Material
References
- For pertinent reviews, see:; a Pellissier H.; Santelli M. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 701–730. [Google Scholar]; b Sanz R. Org. Prep. Proced. Int. 2008, 40, 215–291. [Google Scholar]; c Tadross P. M.; Stoltz B. M. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3550–3577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Gampe C. M.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3766–3778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoermer R.; Kahlert B. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1902, 35, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D.; Simmons H. E. Jr.; Carlsmith L. A.; Vaughan C. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1953, 75, 3290–3291. [Google Scholar]
- For a pertinent review, see:Sletten E. M.; Bertozzi C. R. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6974–6998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For seminal manuscripts regarding cyclohexyne, see:; a Scardiglia F.; Roberts J. D. Tetrahedron 1957, 1, 343–344. [Google Scholar]; b Fixari B.; Brunet J. J.; Caubere P. Tetrahedron 1976, 32, 927–934. [Google Scholar]; c Wentrup C.; Blanch R.; Briehl H.; Gross G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar]
- For seminal manuscripts regarding cyclopentyne, see:; a Wittig G.; Krebs A.; Pohlke R. Angew. Chem. 1960, 72, 324. [Google Scholar]; b Montgomery L. K.; Applegate L. E. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 5305–5307. [Google Scholar]; c Chapman O. L.; Gano J.; West P. R.; Regitz M.; Maas G. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 7033–7036. [Google Scholar]; d Wittig G.; Heyn J. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1969, 726, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- a Allan K. M.; Hong B. D.; Stoltz B. M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4960–4964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Gampe C. M.; Boulos S.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4092–4095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Gampe C. M.; Carreira E. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2962–2965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For a pertinent computational study, see:Sader C. A.; Houk K. N. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 4939–4948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Atanes N.; Escudero S.; Pérez D.; Guitián E.; Castedo L. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3039–3040. [Google Scholar]; b Devlin A. S.; Du Bois J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 1059–1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- For a study pertaining to cyclopentyne, see:Gilbert J. C.; Hou D.-R. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 469–474and references therein. [Google Scholar]
- a Dinges J., Lamberth C., Eds. Bioactive Heterocyclic Compounds Classes: Pharmaceuticals; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, 2012. [Google Scholar]; b Quin L. D.; Tyrell J.. Fundamentals of Heterocyclic Chemistry: Importance in Nature and in the Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- For the aryne distortion model, see:; a Cheong P. H.-Y.; Paton R. S.; Bronner S. M.; Im G.-Y. J.; Garg N. K.; Houk K. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1267–1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Im G.-Y. J.; Bronner S. M.; Goetz A. E.; Paton R. S.; Cheong P. H.-Y.; Houk K. N.; Garg N. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17933–17944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Bronner S. M.; Goetz A. E.; Garg N. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 3832–3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; d Bronner S. M.; Goetz A. E.; Garg N. K. Synlett 2011, 18, 2599–2604. [Google Scholar]; e Goetz A. E.; Bronner S. M.; Cisneros J. D.; Melamed J. M.; Paton R. S.; Houk K. N.; Garg N. K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2758–2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; f Bronner S. M.; Mackey J. L.; Houk K. N.; Garg N. K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13966–13969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; g Goetz A. E.; Garg N. K. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 54–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; h Goetz A. E.; Garg N. K. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 846–851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silyl triflate 9 has also been employed in a Pd-catalyzed cyclotrimerization reaction; see ref (18).
- For the generation of cyclohexyne 3 from an iodonium precursor, see:Fujita M.; Sakanishi Y.; Kim W. H.; Okuyama T. Chem. Lett. 2002, 31, 908–909. [Google Scholar]
- In the absence of CsF, no reaction occurs, which suggests that a mechanism involving cycloaddition followed by elimination of the silyl triflate is not operative.
- a Lovering F.; Bikker J.; Humblet C. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6752–6756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Ritchie T. J.; Macdonald S. J. F. Drug Discovery Today 2009, 14, 1011–1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- No identifiable byproducts were obtained from these reactions; thus, we attribute the loss of mass to substantial nonspecific decomposition.
- Iglesias B.; Peña D.; Pérez D.; Guitián E.; Castedo L. Synlett 2002, 486–488. [Google Scholar]
- For the trapping of arynes with dimethylurea, see:Yoshida H.; Shirakawa E.; Honda Y.; Hiyama T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3247–3249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interestingly, the corresponding trapping experiment involving cyclohexyne precursor 9 in place of 10 failed.
- 3 and 4 have previously been studied computationally (see refs (22) and (24)); however, our efforts mark the first computational study of a 3-substituted cyclohexyne and regioselectivity predictions.
- a Johnson R. P.; Daoust K. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 362–367. [Google Scholar]; b Olivella S.; Pericas M. A.; Riera A.; Sole A. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 52, 4160–4163. [Google Scholar]
- Other stationary points on the potential energy surface of the well-known cyclopentyne to cyclobutylidenecarbene rearrangement were also located. These structures are not relevant for this study, although the moderate yields obtained experimentally suggest competitive processes in which these carbene-like species could be involved. See:Domingo L. R.; Pérez P.; Contreras R. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 498–506. [Google Scholar]
- Olivella S.; Pericas M. A.; Riera A.; Sole A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6884–6888. [Google Scholar]
- In addition to the minimum energy conformer shown in Figure 2, we located another half-chair conformer of 12, which is 0.8 kcal/mol less stable and shows similar distortion with internal angles of 135° and 128° at C1 and C2, respectively.
- Bent H. Chem. Rev. 1961, 61, 275–311. [Google Scholar]
- See the Supporting Information for details.
- Houk K. N.; Sims J.; Watts C. R.; Luskus L. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 7301–7315. [Google Scholar]
- Methyl azide is used as a model for benzyl azide; 12 is used as a model for 14.
- Sawama Y.; Goto R.; Nagata S.; Shishido Y.; Monguchi Y.; Sajiki H. Chem.—Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2631–2636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.