Figure 1. CK2α transcripts levels and localization by WISH.
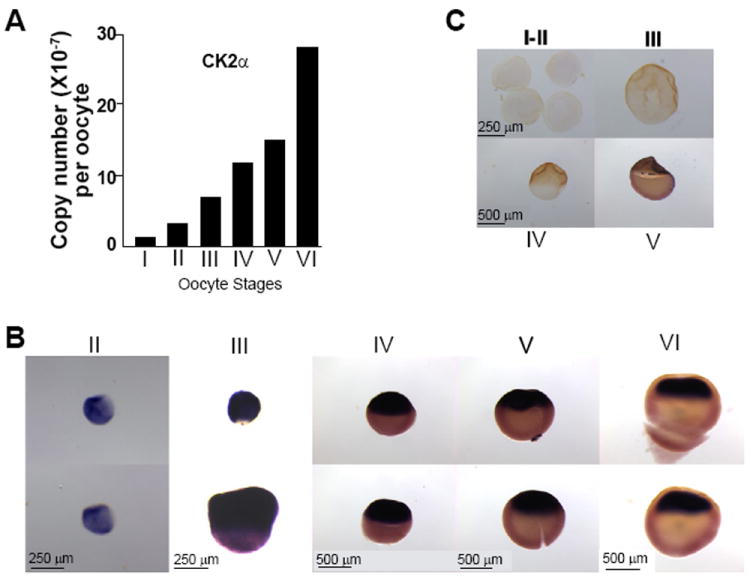
(A) Analysis of total CK2α transcripts in Xenopus oocytes by RT-qPCR. Oocytes were collected, RNA extracted and quantitative PCR was carried out with specific primers to the CK2α coding sequence. The transcript for CK2α increases during oogenesis. This experiment was repeated twice with similar results.
(B,C) Whole mount in situ hybridization of oocytes at different stages with an antisense CK2α -digoxigenin-labeled probe. (B) Chromogenic staining, shown in purple, indicates transcript localization. (C) Representative no probe controls for the in situ hybridizations. Animal hemisphere is up in all panels. Scale bars 250μm or 500μm as indicated in picture. This experiment was repeated using oocytes from three different frogs with similar results.
