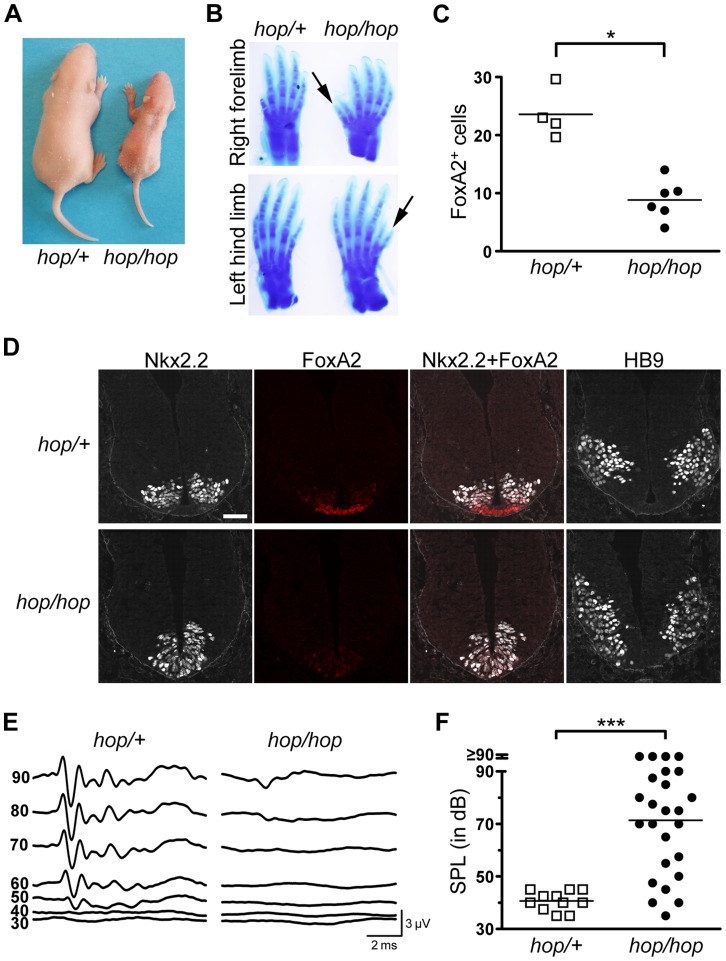
Figure 2. The hop mouse exhibits patterning defects and hearing impairment.
(A) Representative images of hop/+ and hop/hop mice at postnatal day 4. (B) Comparison of Alcian Blue-stained fore and hind limbs of hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Extra digits are indicated by arrows. (C) Statistical analysis of FoxA2-positive cells in the lumbar neural tubes of hop/+ and hop/hop mice (E10.5). Each symbol represents the average number of FoxA2+ cells per focal plane in a single embryo (for each embryo, 12 focal planes in 4 sections were analyzed, Mann-Whitney test: *P = 0.01). (D) Immunostaining of the lumbar neural tube of hop/+ and hop/hop mice (E10.5) with antibodies against the V3 progenitor marker Nkx2.2 (white contrast), the floor plate marker FoxA2 (red), and the motor neuron protein HB9 (white contrast). The hop/hop genotype is associated with reduced FoxA2 expression and ventralization of the Nkx2.2- and HB9-expressing cells. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) Representative ABR waveforms for 3–4 week-old hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Broadband click stimuli were applied at the indicated sound pressure levels (in dB). (F) Statistical analysis of ABR thresholds measured in 3–4 week-old hop/+ and hop/hop mice. Broadband click stimuli between 30 and 90 dB sound pressure level (SPL) were used. Each symbol represents the value for a single mouse (Mann-Whitney test: ***P<0.0001).