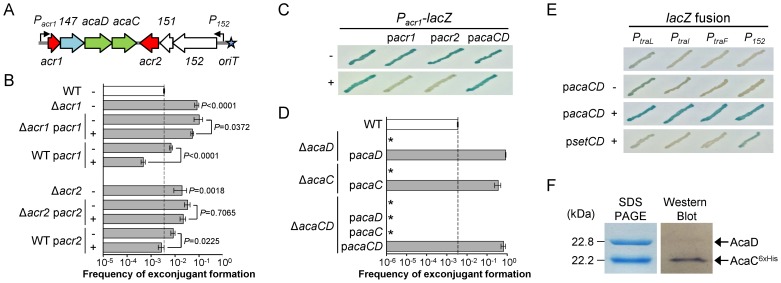
Figure 1. Regulation of IncA/C plasmids.
(A) Schematic representation of the regulatory region of IncA/C plasmids. Genes and promoters are represented by arrowed boxes and angled arrows, respectively. Repressors and activators are shown in red and green, respectively. Genes of unknown function are shown in white and the gene coding for a putative lytic transglycosylase is shown in light blue. Locus names vcrxXXX are abbreviated as XXX. The oriT locus is depicted by a blue star. (B) Effect of the deletion and the overexpression of the negative transcriptional regulator-encoding genes acr1 and acr2. Conjugation assays were carried out using as donors E. coli BW25113 Nx containing pVCR94ΔX2 (WT) or its Δacr1 and Δacr2 mutants. Complementation and overexpression assays were performed with (+) or without (−) arabinose for the expression of acr1 (pacr1) or acr2 (pacr2) from the inducible P BAD promoter. E. coli MG1655 Rf was used as the recipient. Transfer frequencies are expressed as a number of exconjugant per recipient CFUs. The bars represent the mean and standard deviation values obtained from at least three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed on the logarithm value of the means using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test. P-values are indicated next to the bars when comparison referred to WT or next to the brackets when comparing two bars. (C) The constitutive promoter of acr1 (Pacr1) is repressed by Acr1 and Acr2. Activity of Pacr1 was monitored from a single-copy, chromosomally integrated lacZ transcriptional fusion (Pacr1-lacZ). Colorimetric assays were carried out on LB medium supplemented with 40 µg/ml of X-Gal and induction with (+) or without (−) arabinose to express acr1, acr2 or acaCD from P BAD on pacr1, pacr2 or pacaCD, respectively. (D) AcaC and AcaD are essential for conjugative transfer. Transfer assays were carried out using E. coli BW25113 Nx containing pVCR94ΔX2 (WT) or the mutants ΔacaC, ΔacaD or ΔacaCD. Complementation assays were performed by expressing acaC, acaD or acaCD from P BAD on pacaC, pacaD and pacaCD, respectively. Recipient strains and statistical analyses were as described for panel B. All P-values are below 0.0001 when compared to the WT. The asterisk indicates that frequency of exconjugant formation was below the detection limit (<10−8). (E) AcaCD is the direct activator of tra gene promoters. Activity of the PtraL, PtraI, PtraF and P152 was monitored from single-copy, chromosomally integrated lacZ transcriptional fusions. Colorimetric assays were performed as described in panel C with expression of acaCD or setCD from P BAD on pacaCD or psetCD (pGG2B), respectively. (F) AcaD co-purifies with AcaC. Coomassie blue-stained SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of AcaC purified using a Ni-NTA affinity chromatography. AcaD and 6×His-tagged AcaC were co-expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) from pacaDC 6×His. Western blot analysis was performed using a monoclonal antibody against the 6×His-tag.