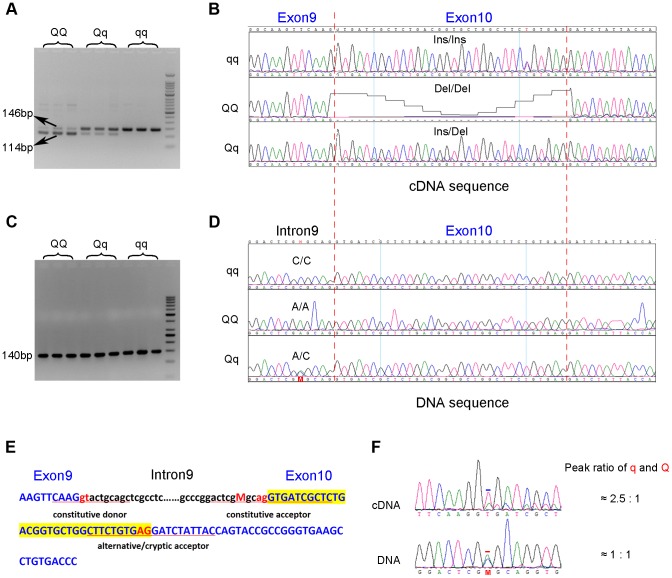
Figure 3. Identification of the g.8283C>A splice mutation in the PHKG1 gene.
(A) RT-PCR products of the PHKG1 gene on a 2.5% agarose gel, amplified from total RNA from animals with different QTL genotypes (QQ, Qq and qq). Two DNA bands of 146 bp and 114 bp with different intensity were observed. (B) Sequence analysis of the RT-PCR products. A 32-bp deletion in exon 10 was detected in QQ and Qq animals. (C) PCR products of the PHKG1 gene on a 2.5% agarose gel, amplified from genomic DNA from animals with different QTL genotypes (QQ, Qq and qq). (D) Sequence analysis of the PCR products. A point mutation (g. 8283C>A) was identified in QQ and Qq individuals. (E) PHKG1 genomic sequence from exon 9 to exon 10. Intronic sequence is in black and lower case, and exonic sequence in blue and upper case. The normal splice-acceptor and -donor sequences (lower case) and the cryptic splice-donor sequences (upper case) are underlined with two red nucleotide letters in the center. The C>A mutation is denoted as “M” in red. (F) Sequence analysis of a heterozygote at the g.8283C>A mutation site. In genomic DNA from a heterozygote, the C and A peaks (the position is indicated by “M” and marked by the red bar) were of equal height in sequence of genomic DNA, as expected. Sequence of the cDNA product from the same heterozygote showed a major peak corresponding to the wild-type sequence and a small peak corresponding to the mutant sequence (the +2 position of exon 10 where the nucleotide T belong to the 32-bp deleted portion is marked by the blue bar).