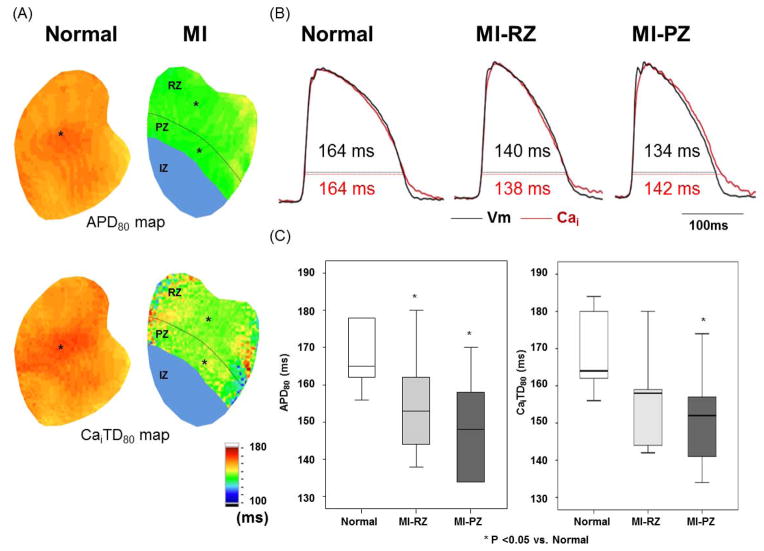
Figure 2.
Action potential duration (APD) and intracellular Ca transient duration (CaiTD) in normal and infarcted ventricles. Measurements were made with PCL of 300 ms in 6 normal and 7 infarct ventricles. A, APD80 map and CaiTD80 map obtained from normal and infarcted ventricles. We divided MI ventricle to three regions. The infarct zone (IZ) has the region distal to coronary ligation. The peri-infarct zone (PZ) was defined as the region within one-third of the distance from the edge of the infarct. The remaining two-thirds of the non-infarcted region was the remote zone (RZ). B, Black and red lines indicate optical tracings of Vm and intracellular calcium (Cai), respectively. The optical tracings were recorded from the site labeled by an asterisk in the APD80 map and CaiTD80 map in A. C, Average of APD80 and CaiTD80 at fixed PCL of 300 ms in normal (N=6) and RZ (N=7) and PZ (N=7). Boxplots were used to compare the median and the range of the data associated with normal ventricles, MI-RZ and MI-PZ. APD80 and CaiTD80 indicate APD and Cai transient duration, respectively, measured at 80% repolarization.