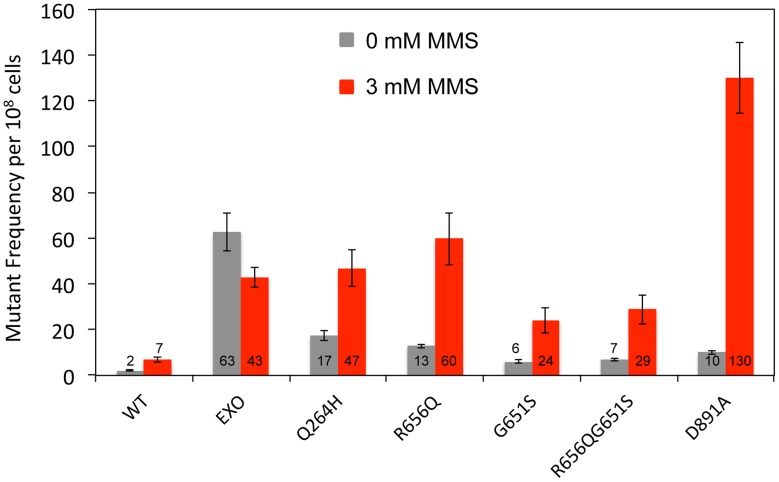
Figure 2. Mutations that disrupted Mip1 polymerase activity caused increased mutant frequency after MMS exposure.
Median frequency (±95% CI) of erythromycin-resistant mutants per 108 rho+ cells of heterozygous diploid strains containing both MIP1 and mip1 with disease-associated mutation, exonuclease disrupting (EXO), or polymerase disrupting mutations in the presence (3 mM) or absence (0 mM) of MMS. Mutant frequencies were determined from at least 20 different independent cultures. CI, confidence interval; MMS, methyl methanesulfonate.