Figure 2.
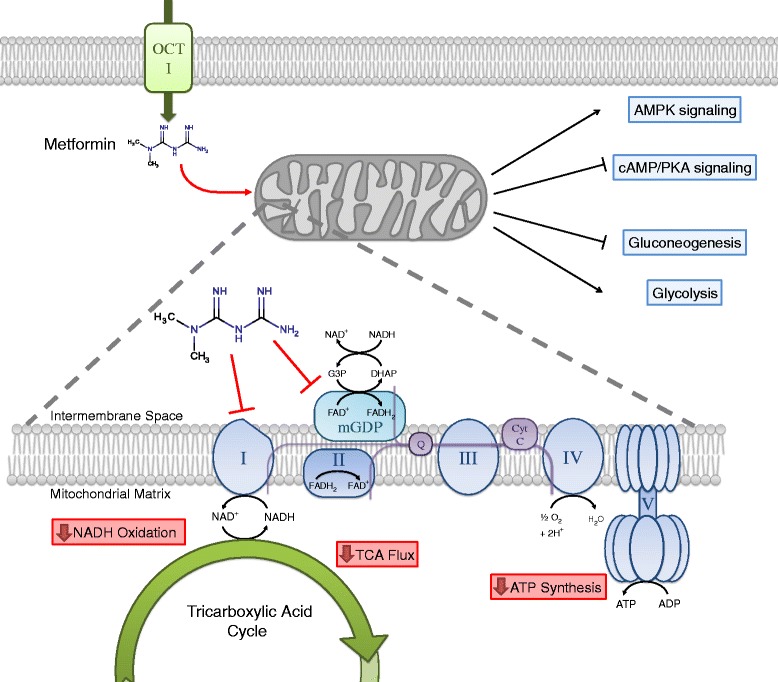
Cellular consequences of metformin action at the mitochondria. Metformin enters the cell by organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1), where it then accumulates in the mitochondria. There, metformin inhibits complex I of the electron transport chain and mGDP, resulting in decreased NADH oxidation. Decreased electron chain activity suppresses tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle flux and decreases mitochondrial ATP synthesis. These actions result in increased AMPK signaling, decreased cAMP/PKA signaling, decreased gluconeogenesis and increased glycolysis.
