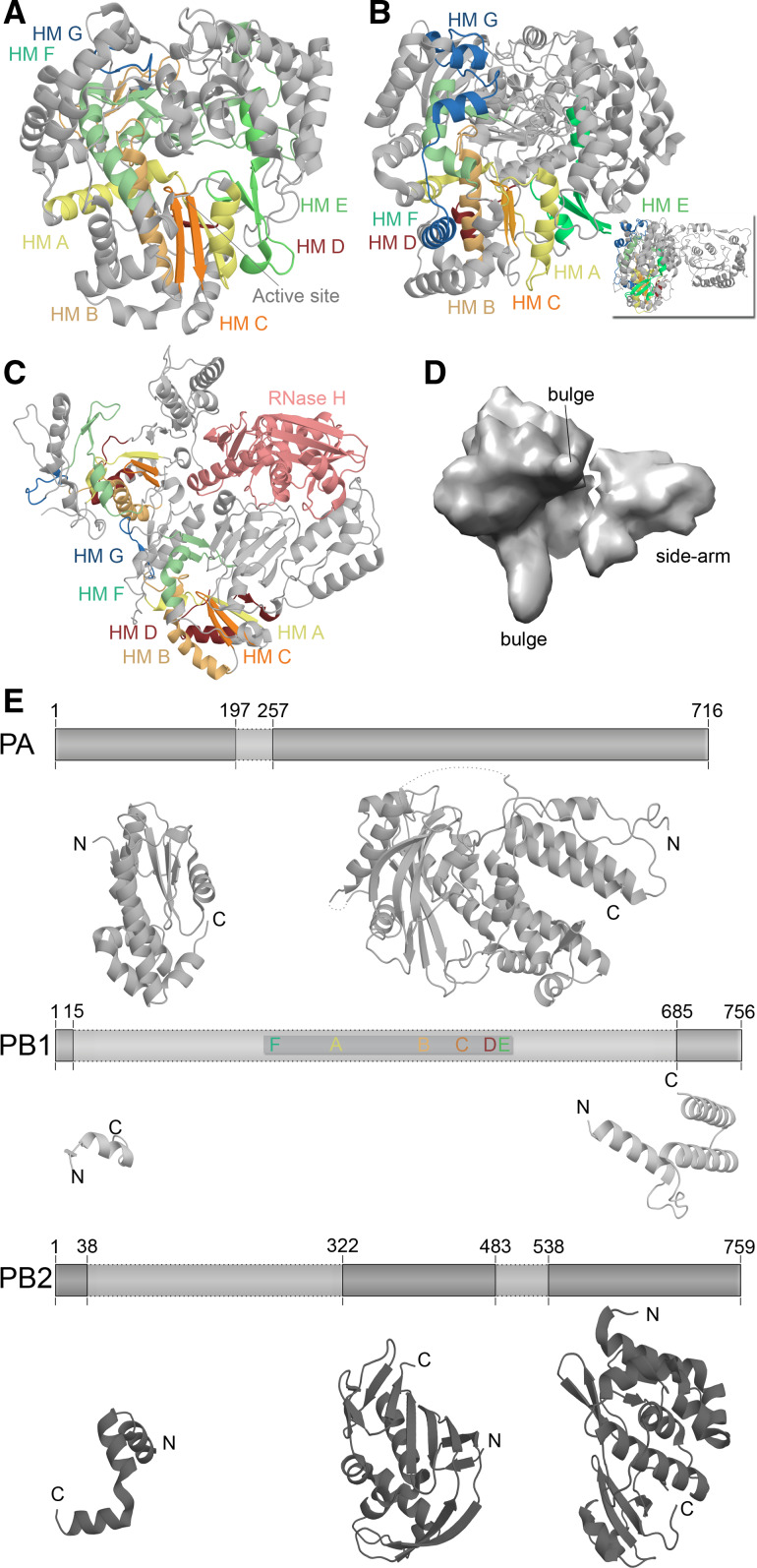
Fig. 4.
Structural differences among RNA virus polymerases. a Structure of the ϕ6 RdRp P2 based on PDB accession 1HI0. b Structure of the JEV polymerase based on PBD entry 4K6 M. Inset depicts 90° rotation of polymerase to visualise the N-terminal methyltransferase domain. c Structure of the HIV-1 RT based on PDB accession 3V4I. The RT is comprised of the p66 (left) and p51 (right) protein subunits. Only the p66 subunit has an RNase domain (pink). Homomorphs A–G are colour coded yellow, gold, orange, red, light green, aquamarine, and blue, respectively in Fig. 4a–c. d EM model of the IAV RdRp based on PDBe entry EMD-2213. Structural features were identified by Moeller et al. [79]. e The IAV polymerase consists of the subunits PA, PB1, and PB2. Six of the seven canonical RNA-dependent polymerase domains motifs are found in PB1, which are colour coded as in Fig. 3. Presently only significant structural information is available for PA and PB2. Figure based on PBD entries 2VY6, 2W69, 2ZNL, 2ZTT, 3EBJ, and 4CB4