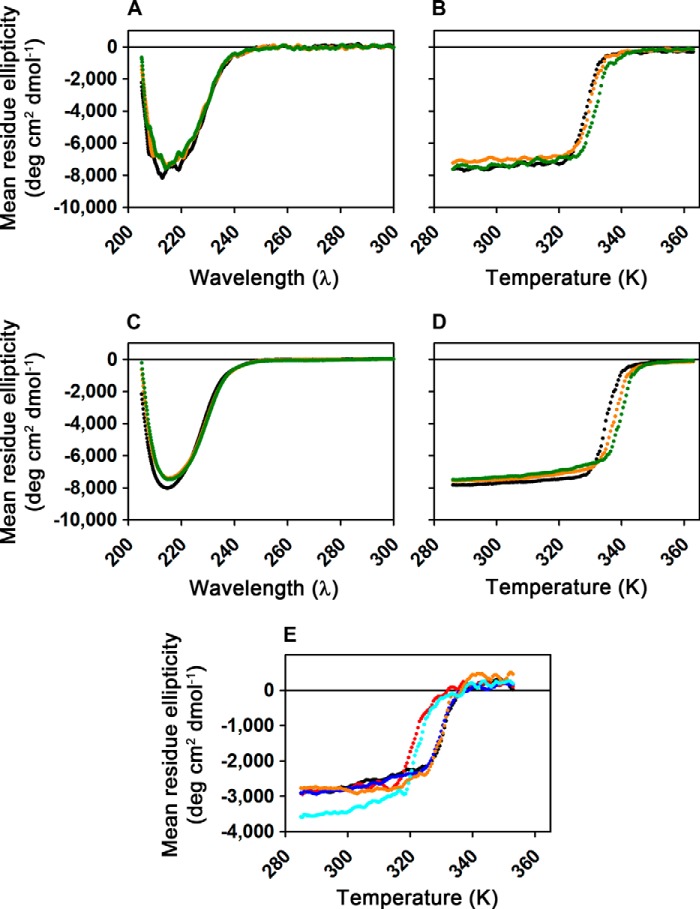
FIGURE 2.
CD spectroscopy demonstrates that wild-type and mutant AlkB-ΔN11 variants are folded in the apo state. A, far-UV CD spectra collected from 1.6 μm WT enzyme at 10 °C either in the absence of ligands (black), in the presence of 200 μm MnCl2 (orange), or in the presence of 200 μm MnCl2 plus 200 μm 2OG (green). Experiments were conducted in demetallated 1H2O buffer containing 75 mm KCl, 50 μm EDTA, 10 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.6. B, thermal denaturation of the samples from A monitored by ellipticity at 217 nm, with the corresponding traces shown in the same colors as in A. Heating at 5 °C/min was initiated shortly after spectral acquisition. C and D, equivalent spectral scans and thermal denaturation experiments to those shown in A and B, respectively, but conducted in demetallated NMR buffer (75 mm KCl, 50 μm EDTA, 50 mm sodium phosphate, pD 5.5, in 99% 2H2O) with 150 μm ZnCl2 substituted for MnCl2. The enzyme is slightly more stable and appears to have somewhat higher affinity for the divalent cation in the deuterated buffer. A minor change in the CD of the protein is observed upon cation binding in this buffer that is not observed in 1H buffer at neutral pH (A). E, thermal denaturation of 1.6 μm WT (black), W89Y (red), M61L (blue), L99M (orange), or I119M (cyan) enzymes monitored by ellipticity at 230 nm. Samples in 1H2O buffer containing 75 mm KCl, 2 mm EDTA, 20 mm HEPES, pH 7.6, were heated at 5 °C/min.