FIGURE 4.
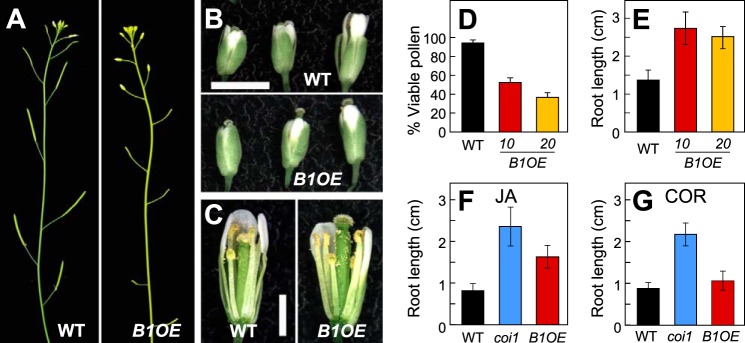
CYP94B1-OE plants display JA-resistant phenotypes in roots and flowers. A, photographs showing silique development in WT (left panel) and CYP94B1-OE (right). B, photographs of representative WT (top panel) and CYP94B1-OE (bottom) flowers at three developmental stages. Scale bar, 2 mm. C, developing stamens and pistils of WT (left) and CYP94B1-OE (right) at time of pollination. Petals and sepals were removed to expose the interior parts of flowers. Scale bar, 1 mm. D, pollen viability of WT and two independent homozygous lines of CYP94B1-OE (B1OE-10 and B1OE-20). Pollen viability was assessed in four independent trials. E - G, root growth inhibition assays. WT, CYP94B1-OE (B1OE), and coi1-1 were grown on MS medium containing either 10 μm jasmonic acid (E, F) or 0.1 μm coronatine (COR) (G). Root length was determined on 10-d (E, F) or 8-d (G) old plants. Data show the mean ± S.D. (n > 20).
