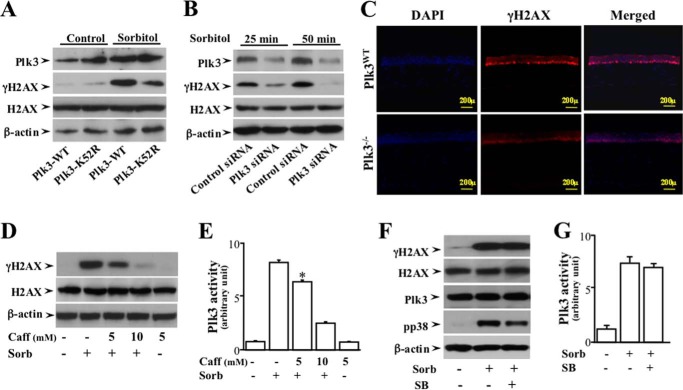
FIGURE 4.
Effects of altered Plk3 activity on hyperosmotic stress-induced γH2AX in HCE cells. A, effect of overexpressing wild type Plk3 and kinase-silencing Plk3k52R mutant on hyperosmotic stress-induced γH2AX in HCE cells. B, effect of knocking down Plk3 mRNAs on hyperosmotic stress-induced Plk3 γH2AX in HCE cells. C, suppression of hyperosmotic stress-induced γH2AX in the epithelial layer of the Plk3-deficient (Plk3−/−) mouse corneas. Immunostaining experiments were performed to detect hyperosmotic stress-induced activation of γH2AX using a γH2AX specific antibody, and cell nuclei were stained by DAPI in corneas of wild type and Plk3−/− knock-out mice. Photo images were taken using a Nikon fluorescent microscope at 10×. D, effect of inhibiting ATM/ATR with Caff (caffeine) on hyperosmotic stress-induced H2AX phosphorylation. E, effect of inhibiting ATM/ATR with Caff on hyperosmotic stress-induced Plk3 activity. F, effects of inhibiting p38 in the absence or presence of 500 μm SB (SB202190, an inhibitor of p38) on hyperosmotic stress-induced ATF-2 phosphorylation. G, effect of hyperosmotic stress on Plk3 activity. Plk3 activity was determined by immunocomplex kinase assay, and the H2AX fusion protein was used as the substrate. The asterisk symbol indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05, n = 3).