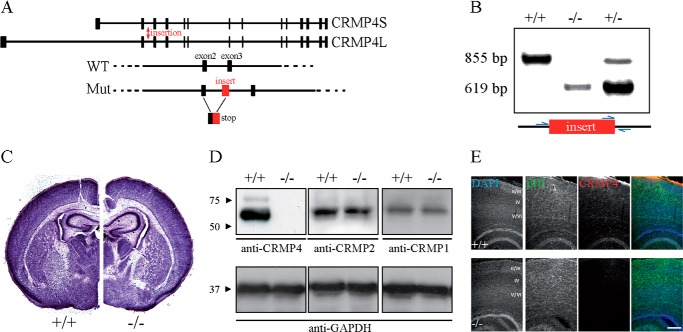
FIGURE 1.
Generation and characterization of CRMP4−/− mice. A, structure of mouse CRMP4 (Dpysl3) gene on chromosome 18 illustrating exons 1–14. The Omnibank 76 trapping vector with a splice acceptor sequence was inserted after exon 2 of the CRMP4 gene (red arrow). This insertion results in incorrect splicing of CRMP4 mRNA such that all downstream exons are not expressed. B, genotyping of CRMP4 mice using PCR amplification of DNA isolated from tails with specific primers (blue arrows). The wild-type allele yields an 855-bp fragment, whereas the knock-out allele yields a 619-bp fragment. C, Nissl staining of 50-μm-thick coronal sections from P5 mice at the level of the ventromedial hypothalamus. Brain cytoarchitecture is similar in the CRMP4−/− and CRMP4+/+ littermate controls. D, Western blot analysis of brain lysates from P5 CRMP4+/+ and CRMP4−/− mice with anti-CRMP4, anti-CRMP1, anti-CRMP2, or anti-GAPDH antibodies. E, sagittal sections of P5 mouse brain from wild-type CRMP4+/+ and CRMP4−/− mice stained with DAPI and anti-βIII-tubulin and anti-CRMP4 antibodies. Scale bar, 250 μm.