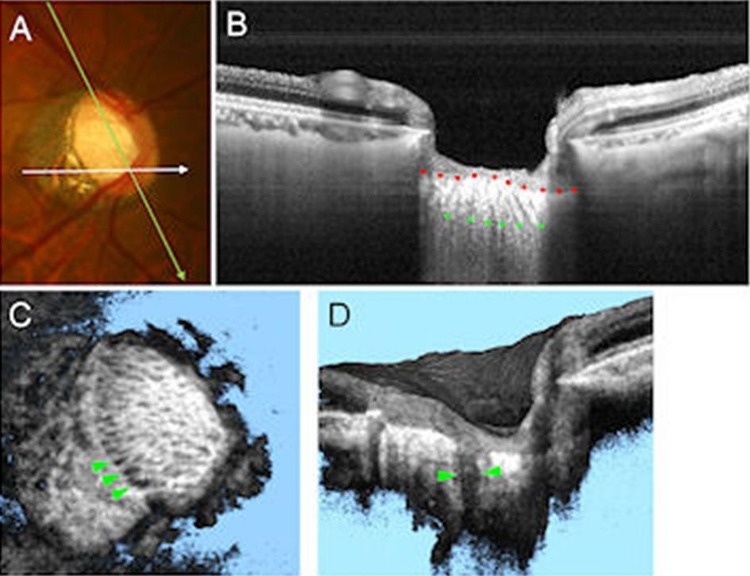
Figure 1.
Swept source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) for assessing the lamina cribrosa (LC) defects. (A) Colour disc photograph shows orientations of the SS-OCT scan. (B) B-scan image averaging multi-scan frames at green line in (A), with the anterior (red dots) and posterior border (green dots) of the LC delineated. The LC pores are also visualised as hyporeflective lines in LC. (C) The SS-OCT C-mode image reconstructed from raster scan. The laminar pores are visualised as hyporeflective spots on the en face image. The LC defects are shown by green arrowheads as hyporeflective lesions. (D) The SS-OCT sectioned volume image oriented by white line in (A). The LC defects are shown by green arrowheads as a hyporeflective line, which shows full-thickness loss of the lamina reflectivity on B-scan image.