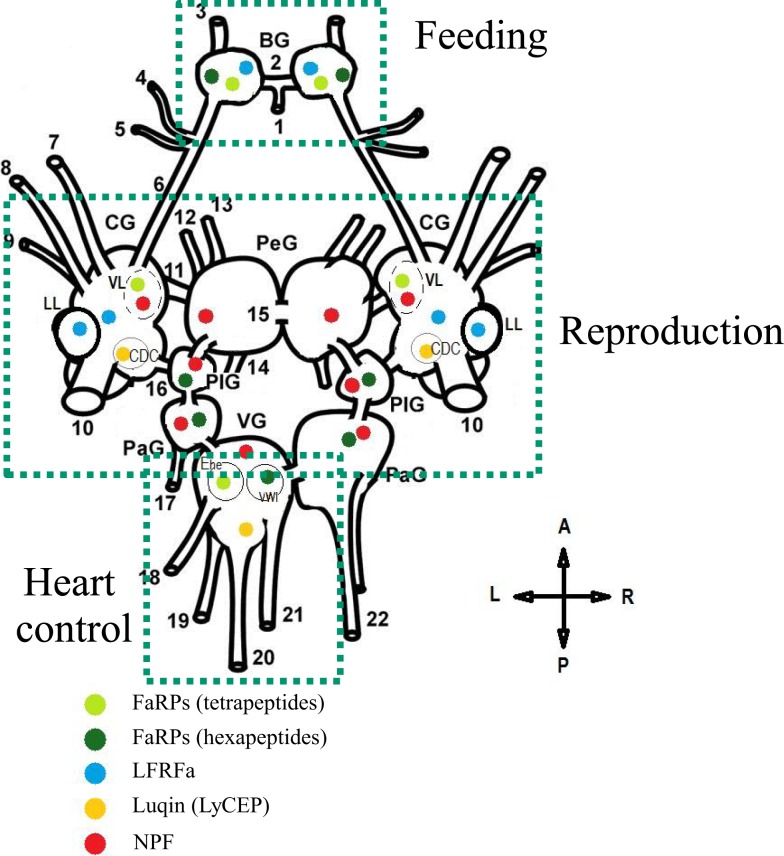
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the distribution and the role of distinct RFamide-like peptides (FLPs) in the central nervous system (dorsal view) of Lymnaea stagnalis. BG, buccal ganglion; CG, cerebral ganglion; PeG, pedal ganglion; PlG, pleural ganglion; PaG, parietal ganglion; VG, visceral ganglion; VL, ventral lobe; LL, lateral lobe; CDC, caudo-dorsal cell. Nerves: 1, postbuccal; 2, buccal commissure; 3, dorsobuccal; 4, laterobuccal; 5, ventrobuccal; 6, cerebro-buccal connective; 7, superior lip; 8, median lip; 9, tentacular; 10, cerebral commissure; 11, cerebro-pedal connective; 12, superior medial; 13, median pedal; 14, inferior pedal; 15, pedal commissure; 16, cerebro-pleural connective; 17, left parietal; 18, cutaneous; 19, anal; 20, intestinal; 21, genital; 22, right parietal. Ehe neuron and the visceral white interneuron (VWI) [Adapted from Ref. (72, 104, 130, 141, 142)].