Figure 1. Structure of GPCRs in complex with allosteric modulators.
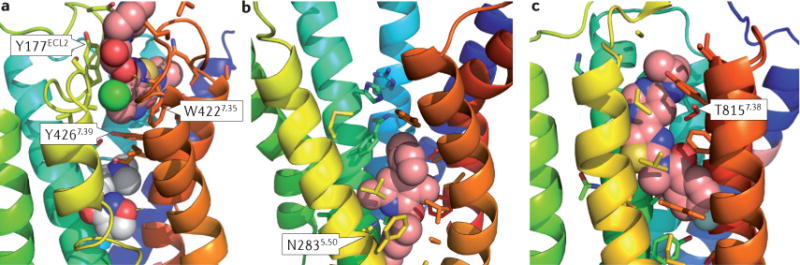
a | Interaction of a class A GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor) — the M2 subtype muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (Protein Data Bank (PDB) identifier: 4MGT) — in complex with the positive allosteric modulator (PAM) LY2119620 (pink) and the orthosteric ligand iperoxo (white). Y177 and W422 engage the PAM via π–π interactions. Y426 separates the allosteric ligand binding site from the orthosteric ligand binding site. b | Interaction of the class B corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 1 (CRF1 receptor) with the allosteric antagonist CP-376395 (pink; PDB 4K5Y). The binding pocket in the intracellular half of the seven- transmembrane domain is dominated by hydrophobic interactions. The conserved N283 forms a crucial hydrogen bond with the ligand. c | Interaction of the class C metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (PDB 4OR2) with the negative allosteric modulator FITM (pink). The binding pocket overlaps with the orthosteric ligand binding site in class A GPCRs. It is largely hydrophobic, with T815 contributing an important hydrogen bond to the ligand.
