Fig. 1.
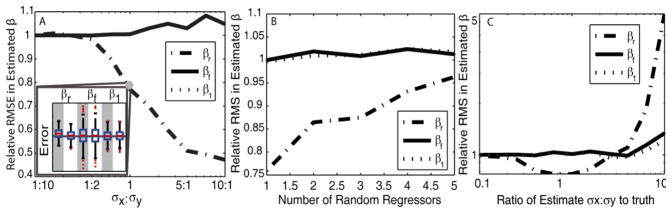
The relative RMSEs of Model II to OLS for each estimated coefficient (βr, βf, β1) are plotted as a function of the ratio of the true standard deviations, σx:σy (A), the number of random regressors, (B) and the accuracy of the ratio estimate (C). With increasing σx:σy ratios, model II regression has increased relative accuracy in βr estimates compared to OLS with increasing σx:σy ratios. Comparison of the βf, βr, and β1 error distributions formed is shown explicitly in the inlay for the point σx/σy =1 in (A). The gray column shows the OLS error and the white column shows the Model II error, the horizontal line is where the error is zero. In (C), for one unit σy, the estimated ratio μx was allowed to deviate from the ideal case, μx/σx = 1. The common point shared in (A, B, C) is located in (B) at ‘Number of Random Regressors’ = 1, and (C) at ‘Ratio of Estimate to Truth’ = 1.
