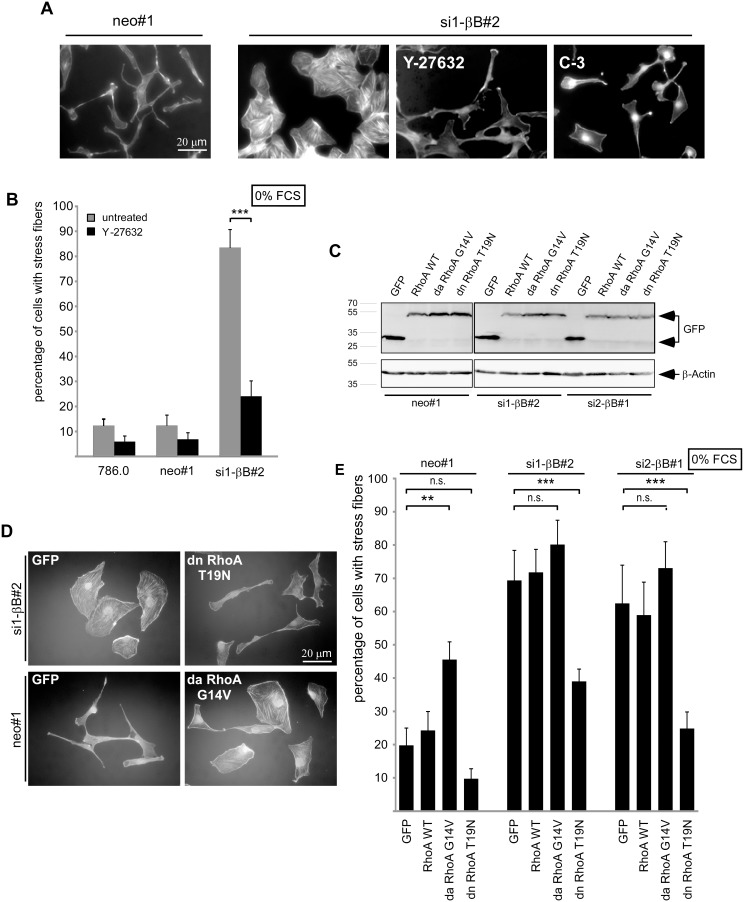
Figure 4. The RhoA pathway is required for actin stress fiber formation induced by Activin B knockdown.
(A) TRITC-labeled Phalloidin staining of serum starved (0% FCS) neo#1 control cells and si1-βB#2 Activin B knockdown cells either untreated or treated with a Rho-Kinase inhibitor (Y-27632) or a Rho inhibitor (C3-Exoenzyme). (B) Quantification of untreated (grey bars) and Y-27632 treated (black bars) cells with actin stress fibers. (C) Generation of pools of 786.0 neo#1 and Activin B knockdown clones (si1-βB#2, si2-βB#1) stably transfected with EGFP empty vector, expression constructs for GFP-tagged wildtype RhoA, dominant active RhoA (G14V) or dominant negative RhoA (T19N). Expression of EGFP and GFP-tagged RhoA proteins was confirmed by Western Blotting. (D) TRITC-labeled Phalloidin staining of the indicated pools after serum starvation (0% FCS) for 3 hours. (E) Quantification of cells with actin stress fibers upon serum starvation for 3 hours. Bars represent the mean of three (B) or five (E) independent experiments, error bars indicate standard deviation. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test (4B) and ANOVA analysis (4E) and denoted by asterisks: **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; n.s. not significant.