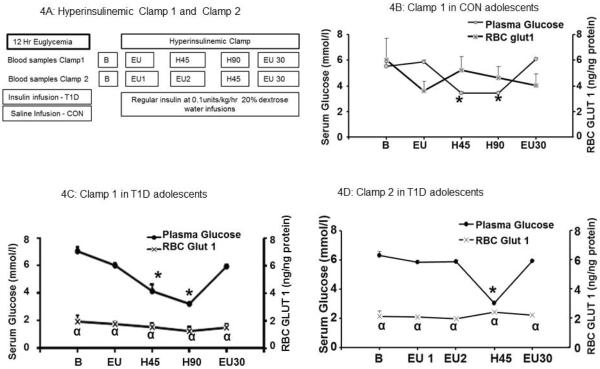
Figure 4. Hyperinsulinemic clamp studies in T1D and CON groups.
4A: The schematic diagram for clamp 1 and clamp 2 studies.
4B: Hyperinsulinemic clamp I study in CON children (n=8). Left y axis demonstrates the serum glucose concentration in mmol/l and right y-axis indicates the RBC GLUT1 concentrations in ng/ng protein. The x-axis shows time points B, baseline; EU, euglycemia; H45 and H90 min, after 45 and 90 minutes of hypoglycemia; and EU30, after 30 min of return to euglycemia.
4C: Hyperinsulinemic clamp I study in T1D children (n=8). The left y-axis demonstrates serum glucose in mmol/L and right y-axis indicates RBC GLUT1 in ng/ng. B, The x-axis shows time points B, baseline; EU, euglycemia; H45 and H90 min, after 45 and 90 minutes of hypoglycemia; and EU30, after 30 min of return to euglycemia
4D: Hyperinsulinemic clamp II study in T1D children (n=8). Left x-axis demonstrates the serum glucose concentration in mmol/L and right y-axis indicates RBC GLUT1 concentrations in ng/ng protein. The x-axis shows time points : B, baseline; EU1 and EU2, after 60 and 120 minutes of euglycemia; H, during hypoglycemia; and EU30, after 30 min of return to euglycemia., * p<0.0001 Serum glucose values compared to the baseline serum glucose values for each group. α p<0.001 RBC GLUT1 concentration in T1D group compared to the corresponding RBC GLUT1 concentration in the CON group.