Figure 2.
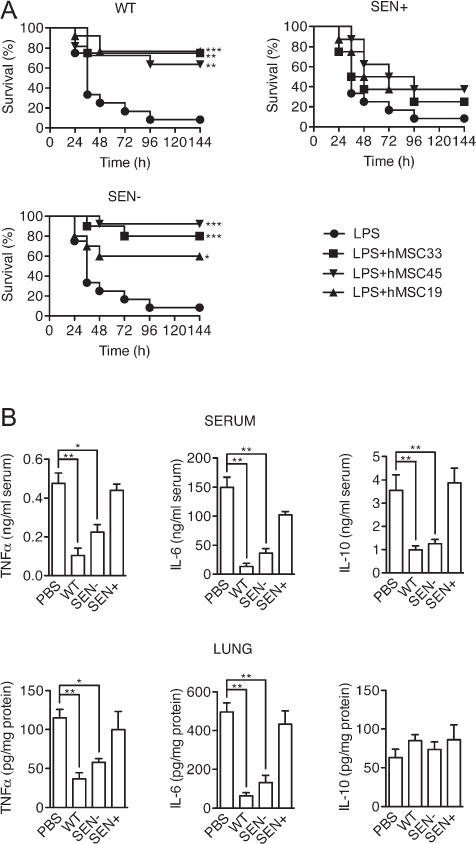
Senescent hMSCs fail to protect against lethal sepsis. Mice (10 mice/group) were injected i.p. with LPS (400 μg/mouse) and treated i.p. with PBS or 106 hMSCs 30 minutes later. Three different hMSC isolates (hMSC19, 33, and 44) were used. WT, wild-type primary hMSCs; SEN+, gamma-irradiated hMSCs; SEN−, telomerase-immortalized hMSCs. (A): Survival was monitored every 12 hours. (B): Cytokine levels were determined by ELISA in protein extracts from blood serum and lung collected 6 hours after LPS injection (n = 5). *, p < .05; **, p < .01; ***, p < .005, versus controls with LPS alone. Error bars represent SEM. Abbreviations: hMSC, human mesenchymal stem cell; LPS, lipopolysaccharide PBS, phosphate buffered saline.
