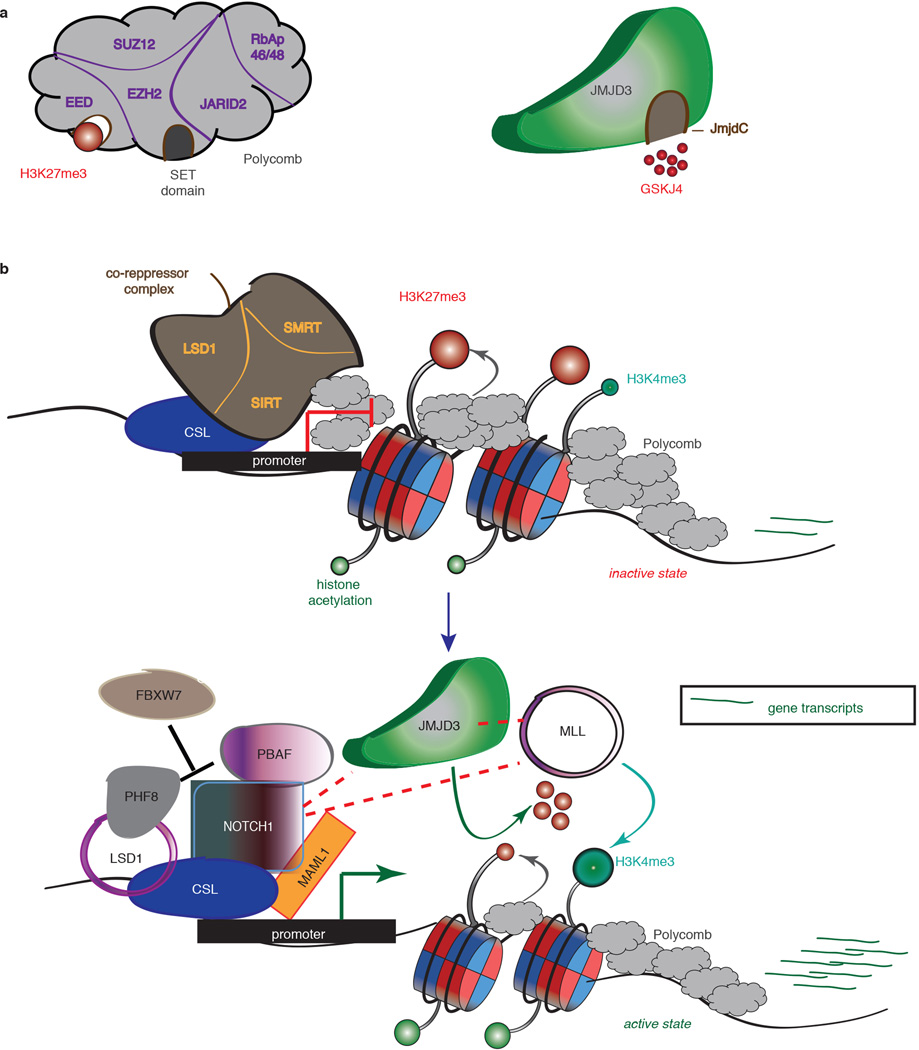
Extended Data Figure 10. JMJD3 as a pivotal factor in NOTCH1-mediated oncogenic activation in T cell leukemia.
a, Schematic representation of the H3K27me3 writer (polycomb complex, right panel) and eraser JMJD3 (left panel). EZH2 entails the catalytic subunit of the complex through its SET domain, whereas EED subunit recognizes the H3K27me3 mark and helps polycomb binding. JmjC domain activity is inhibited by the small molecule inhibitor GSKJ4. b, Main notion of the key role of JMJD3 in the NOTCH1 transcriptional complex’ Before activation of the NOTCH1 signaling pathway the promoters of classical NOTCH1 targets are bound by RBBJk together with components of the co-repressor complexes and poycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), leading to low gene expression. After binding of NOTCH1 and its co-activator MAML1 the genes are activated through recruitment of JMJD3 and MLL complex, with simultaneous eviction of PRC2, which leads to demethylation of H3K27me3 and methylation of H3K4me3.