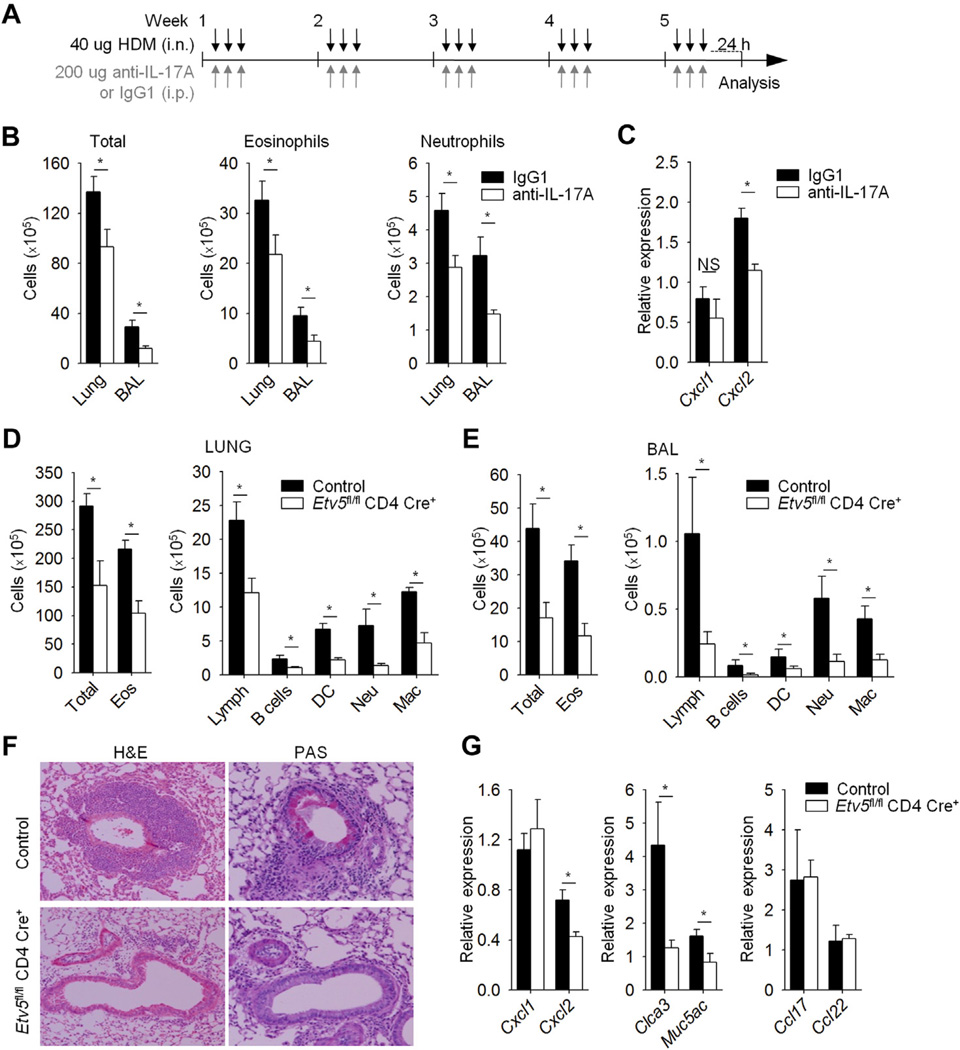
FIG 3.
Etv5 mutant mice have reduced HDM-induced allergic airway inflammation. A, Wild-type mice were immunized (intranasally [i.n.]) with HDM for 5 weeks to induced allergic inflammation and treated with anti–IL-17A or IgG1 antibodies (intraperitoneally [i.p.]). B, Total and inflammatory cell counts in the lungs and BAL fluid of HDM-induced airway inflammation in wild-type mice. C, Total cells from lungs of wild-type mice were used for gene expression analysis by means of qRT-PCR. D-G, Control and Etv5 mutant mice were sensitized and challenged (intranasally) with HDM for 5 weeks to induce allergic inflammation. Inflammatory cells in the lung tissue and BAL fluid of control and Etv5 mutant mice were as follows: DC, dendritic cells; Eos, eosinophils; Lymph, lymphocytes; Mac, macrophages; Neu, neutrophils. Fig 3, F, Cell infiltration in the lungs and mucus in the airways of control and Etv5 mutant mice were evaluated by means of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining. Fig 3, G, Total cells from lungs of control and Etv5 mutant mice were used for gene expression analysis by means of qRT-PCR. Data are means ± SEMs of 5 to 6 mice per group (Fig 3, A-G) and representative of 2 independent experiments with similar results. *P < .05. NS, Not significant.